The Combined Effects of Social Determinants of Health on Childhood Overweight and Obesity
- PMID: 36989504
- PMCID: PMC12344120
- DOI: 10.1089/chi.2022.0222
The Combined Effects of Social Determinants of Health on Childhood Overweight and Obesity
Abstract
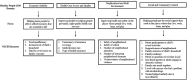
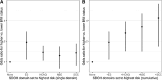
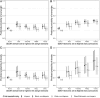
Background: To characterize the association between multiple social determinants of health (SDOH) and overweight and obesity among US children. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using the 2016-2020 National Survey of Children's Health. SDOH domains consisted of Economic Stability, Social and Community Context, Neighborhood and Built Environment, and Health Care Access and Quality. We used ordinal logistic regression to model associations between SDOH and weight status and calculate predicted probabilities of having overweight or obesity for various SDOH profiles. Results: Data from 81,716 children represented a weighted sample of 29,415,016 children ages 10-17 years in the United States. Of these, 17% had overweight and 17% had obesity. Compared with children with the theoretically lowest-risk SDOH profile, children with the highest-risk SDOH profiles in all four domains had an odds ratio of having a higher BMI category of 4.38 (95% confidence interval 1.67-7.09). For the lowest risk profile, the predicted probability of obesity varied from 8% to 11%, depending on race. For the highest risk profile, the predicted probability of obesity varied from 26% to 34%, depending on race. Conclusions: While high-risk values in each SDOH domain were associated with higher predicted probability of overweight and obesity, it was the combination of highest risk values in all the SDOH domains that led to greatest increases. This suggests a complex and multilayered relationship between the SDOH and childhood obesity, necessitating a comprehensive approach to addressing health equity to reduce childhood obesity.
Keywords: childhood obesity; disparities; social determinants of health.
Figures
References
-
- Healthy People 2030. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Available from: https://health.gov/healthypeople/priority-areas/social-determinants-health [Last accessed: July 5, 2022].
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

