Efficient Labeling of Vesicles with Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes via the Salt-Change Method
- PMID: 36990442
- PMCID: PMC10100391
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05166
Efficient Labeling of Vesicles with Lipophilic Fluorescent Dyes via the Salt-Change Method
Abstract
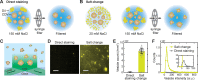
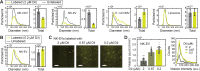
Fluorescent labeling allows for imaging and tracking of vesicles down to single-particle level. Among several options to introduce fluorescence, staining of lipid membranes with lipophilic dyes provides a straightforward approach without interfering with vesicle content. However, incorporating lipophilic molecules into vesicle membranes in an aqueous solution is generally not efficient because of their low water solubility. Here, we describe a simple, fast (<30 min), and highly effective procedure for fluorescent labeling of vesicles including natural extracellular vesicles. By adjusting the ionic strength of the staining buffer with NaCl, the aggregation status of DiI, a representative lipophilic tracer, can be controlled reversibly. Using cell-derived vesicles as a model system, we show that dispersion of DiI under low-salt condition improved its incorporation into vesicles by a factor of 290. In addition, increasing NaCl concentration after labeling induced free dye molecules to form aggregates, which can be filtered and thus effectively removed without ultracentrifugation. We consistently observed 6- to 85-fold increases in the labeled vesicle count across different types of dyes and vesicles. The method is expected to reduce the concern about off-target labeling resulting from the use of high concentrations of dyes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): M.C., Y.B., D.W.H., J.E.P., S.W.O., and M.J.S. filed a patent on the vesicle labeling method described in this study.
Figures


References
-
- van der Vlist E. J.; Nolte-’t Hoen E. N. M.; Stoorvogel W.; Arkesteijn G. J. A.; Wauben M. H. M. Fluorescent Labeling of Nano-Sized Vesicles Released by Cells and Subsequent Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis by High-Resolution Flow Cytometry. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7 (7), 1311–1326. 10.1038/nprot.2012.065. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Görgens A.; Bremer M.; Ferrer-Tur R.; Murke F.; Tertel T.; Horn P. A.; Thalmann S.; Welsh J. A.; Probst C.; Guerin C.; Boulanger C. M.; Jones J. C.; Hanenberg H.; Erdbrügger U.; Lannigan J.; Ricklefs F. L.; El-Andaloussi S.; Giebel B. Optimisation of Imaging Flow Cytometry for the Analysis of Single Extracellular Vesicles by Using Fluorescence-Tagged Vesicles as Biological Reference Material. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8 (1), 1587567.10.1080/20013078.2019.1587567. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

