Resting-state functional connectivity in multiple sclerosis patients receiving nabiximols for spasticity
- PMID: 36991352
- PMCID: PMC10052832
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-023-03171-0
Resting-state functional connectivity in multiple sclerosis patients receiving nabiximols for spasticity
Abstract
Background: Nabiximols (Sativex®) is a cannabinoid approved for multiple sclerosis (MS)-related spasticity. Its mechanism of action is partially understood, and efficacy is variable.
Objective: To conduct an exploratory analysis of brain networks connectivity changes on resting state (RS) functional MRI (fMRI) of MS patients treated with nabiximols.
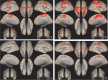
Methods: We identified a group of MS patients treated with Sativex® at Verona University Hospital, who underwent RS brain fMRI in the 4 weeks before (T0) and 4-8 weeks after (T1) treatment start. Sativex® response was defined as ≥ 20% spasticity Numerical Rating Scale score reduction at T1 vs. T0. Connectivity changes on fMRI were compared between T0 and T1 in the whole group and according to response status. ROI-to-ROI and seed-to-voxel connectivity were evaluated.
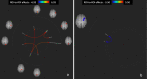
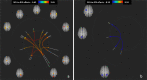
Results: Twelve MS patients (7 males) were eligible for the study. Seven patients (58.3%) resulted Sativex® responders at T1. On fMRI analysis, Sativex® exposure was associated with global brain connectivity increase (particularly in responders), decreased connectivity of motor areas, and bidirectional connectivity changes of the left cerebellum with a number of cortical areas.
Conclusions: Nabiximols administration is associated with brain connectivity increase of MS patients with spasticity. Modulation of sensorimotor cortical areas and cerebellum connectivity could play a role in nabiximols effect.
Keywords: Cannabinoid; Functional MRI; Multiple sclerosis; Nabiximols; Spasticity; Symptomatic therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests related to this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Novotna A, Mares J, Ratcliffe S, Novakova I, Vachova M, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, enriched-design study of nabiximols (Sativex®), as add-on therapy, in subjects with refractory spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18(9):1122–1131. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03328.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carotenuto A, Valsasina P, Schoonheim MM, et al. Investigating functional network abnormalities and associations with disability in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2022;99(22):e2517–e2530. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

