Pre-referral rectal artesunate is no "magic bullet" in weak health systems
- PMID: 36991404
- PMCID: PMC10060914
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-02777-y
Pre-referral rectal artesunate is no "magic bullet" in weak health systems
Abstract
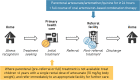
Severe malaria is a potentially fatal condition that requires urgent treatment. In a clinical trial, a sub-group of children treated with rectal artesunate (RAS) before being referred to a health facility had an increased chance of survival. We recently published in BMC Medicine results of the CARAMAL Project that did not find the same protective effect of pre-referral RAS implemented at scale under real-world conditions in three African countries. Instead, CARAMAL identified serious health system shortfalls that impacted the entire continuum of care, constraining the effectiveness of RAS. Correspondence to the article criticized the observational study design and the alleged interpretation and consequences of our findings.Here, we clarify that we do not dispute the life-saving potential of RAS, and discuss the methodological criticism. We acknowledge the potential for confounding in observational studies. Nevertheless, the totality of CARAMAL evidence is in full support of our conclusion that the conditions under which RAS can be beneficial were not met in our settings, as children often failed to complete referral and post-referral treatment was inadequate.The criticism did not appear to acknowledge the realities of highly malarious settings documented in detail in the CARAMAL project. Suggesting that trial-demonstrated efficacy is sufficient to warrant large-scale deployment of pre-referral RAS ignores the paramount importance of functioning health systems for its delivery, for completing post-referral treatment, and for achieving complete cure. Presenting RAS as a "magic bullet" distracts from the most urgent priority: fixing health systems so they can provide a functioning continuum of care and save the lives of sick children.The data underlying our publication is freely accessible on Zenodo.
Keywords: Antimalarials; Artesunate; Case management; Effectiveness; Health systems; Quality of care; Rectal artesunate; Referral; Severe malaria.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Comment on
-
Effectiveness of rectal artesunate as pre-referral treatment for severe malaria in children under 5 years of age: a multi-country observational study.BMC Med. 2022 Oct 11;20(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02541-8. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36217159 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Management of severe malaria: a practical handbook. 3. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for the treatment of malaria –. 3. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Gomes MF, Faiz MA, Gyapong JO, Warsame M, Agbenyega T, Babiker A, Baiden F, Yunus EB, Binka F, Clerk C, et al. Pre-referral rectal artesunate to prevent death and disability in severe malaria: a placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):557–566. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61734-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Malaria Report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

