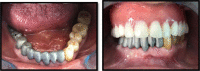
Impact of unilateral removable partial dentures versus removable partial dentures with major connector on oral health-related quality of life of elder patients: a clinical study
- PMID: 36991435
- PMCID: PMC10061744
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-02870-x
Impact of unilateral removable partial dentures versus removable partial dentures with major connector on oral health-related quality of life of elder patients: a clinical study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to establish the survival rate of unilateral removable partial dentures (u-RPD) comparative with bilateral RPD (bi-RPD) with major connector in elder patients, as well as to determine both their treatment satisfaction and oral health.
Methods: The study sample included 17 patients treated with u-RPD and 17 patients treated with bi-RPD with a major connector. The patients were followed over five years with recalls every 6 months. A 5- points Likert scale was used to determine the satisfaction of the patients. The Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14) questionnaire was used to evaluate their oral health after each type of administrated treatment. The local oral examined aspects included the maintenance of the abutment teeth periodontal health, the fractures of the removable dentures, the fractures of the connectors, the chipping of the aesthetic material. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted to evaluate the performance of the two treatments.
Results: The mean survival time in years was 4.882 ± 0.114, 95% CI (4.659; 5.106) and 4.882 ± 0.078, 95% CI (4.729; 5.036), for the u-RPD and the bi-RPD, respectively. The five-year survival rates for the two dentures were 94.1% for u-RPD vs. 88.2% for bi-RPD with a major connector, without a statistically significant difference between them (Log-rank test χ2(1) = 0.301, p = 0.584). The patients receiving u-RPD presented significantly higher satisfaction scores compared to the patients receiving bi-RPD, 4.88 ± 0.48 vs. 4.41 ± 0.62, Mann-Whitney U test, p = 0.026.
Conclusion: Patients receiving u-RPD presented higher levels of treatment satisfaction and better oral health than patients receiving bi-RPD. The survival rates of the treatments u-RPD and bi-RPD were similar.
Keywords: Oral health; Patient satisfaction; Quality of life; Removable partial dentures; Survival analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goguţă LM, Ioanaş A, Jivanescu A. Geriatric patients’ psychological status relative to the removable prosthodontic treatment. Eur Geriatr Med. 2017;8(5–6):483–5. doi: 10.1016/j.eurger.2017.07.024. - DOI
-
- Arce-Tumbay Jackelyn / Sánchez-Ayala, Alfonso / Sotto-Maior, Bruno Salles / Senna, Plinio Mendes / Campanha, Nara Hellen. Mastication in subjects with extremely shortened Dental Arches rehabilitated with removable partial dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 2011;6:24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources