Reducing Noise, Artifacts and Interference in Single-Channel EMG Signals: A Review
- PMID: 36991639
- PMCID: PMC10059683
- DOI: 10.3390/s23062927
Reducing Noise, Artifacts and Interference in Single-Channel EMG Signals: A Review
Abstract
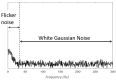
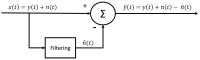
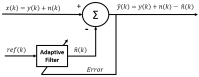
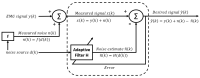
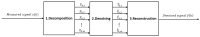
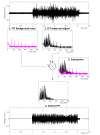
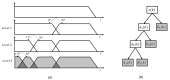
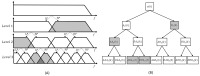
Electromyography (EMG) is gaining importance in many research and clinical applications, including muscle fatigue detection, control of robotic mechanisms and prostheses, clinical diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases and quantification of force. However, EMG signals can be contaminated by various types of noise, interference and artifacts, leading to potential data misinterpretation. Even assuming best practices, the acquired signal may still contain contaminants. The aim of this paper is to review methods employed to reduce the contamination of single channel EMG signals. Specifically, we focus on methods which enable a full reconstruction of the EMG signal without loss of information. This includes subtraction methods used in the time domain, denoising methods performed after the signal decomposition and hybrid approaches that combine multiple methods. Finally, this paper provides a discussion on the suitability of the individual methods based on the type of contaminant(s) present in the signal and the specific requirements of the application.
Keywords: artifact; contaminant reduction; denoising; electromyography; filtering; interference; noise; signal processing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition Combined With Notch Filtering for Interpretation of Surface Electromyograms During Functional Electrical Stimulation.IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017 Aug;25(8):1268-1277. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2016.2624763. Epub 2016 Nov 3. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017. PMID: 27834646 Clinical Trial.
-
A Review of Techniques for Surface Electromyography Signal Quality Analysis.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2023;16:472-486. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2022.3164797. Epub 2023 Jan 5. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 35380969 Review.
-
Denoising of the gradient artifact present in simultaneous studies of muscle blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) signal and electromyography (EMG).Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Sep;111:179-185. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2024.05.004. Epub 2024 May 7. Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38723782
-
Removal of ECG Artifacts Affects Respiratory Muscle Fatigue Detection-A Simulation Study.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 23;21(16):5663. doi: 10.3390/s21165663. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451104 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Review of the Algorithms for Removal of Electrocardiographic Interference from Trunk Electromyography.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 29;20(17):4890. doi: 10.3390/s20174890. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32872470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Self-report, Palpation, and Surface Electromyography Dataset During Isometric Muscle Contraction.Sci Data. 2024 Feb 15;11(1):208. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03030-8. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38360835 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic measurement of short-term variability of repolarization captures modulation by pacing on human electrograms.Heart Rhythm O2. 2025 Mar 14;6(6):854-863. doi: 10.1016/j.hroo.2025.03.005. eCollection 2025 Jun. Heart Rhythm O2. 2025. PMID: 40717856 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Muscle Fatigue Degree in Cyclical Movements Based on the High-Frequency Components of sEMG.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 May 6;10(5):291. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10050291. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422121 Free PMC article.
-
An Onset Detection Method for Slowly Activated Muscle Based on Marginal Spectrum Entropy.Sensors (Basel). 2025 May 8;25(10):2963. doi: 10.3390/s25102963. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431759 Free PMC article.
-
Wavelet Analysis of Respiratory Muscle sEMG Signals during the Physiological Breakpoint of Static Dry End-Expiratory Breath-Holding in Naive Apneists: A Pilot Study.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 16;23(16):7200. doi: 10.3390/s23167200. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan B., Saad I., Bolong N., Siew K.E. A Review of Surface EMG in Clinical Rehabilitation Care Systems Design; Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 19th Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD); Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia. 23–25 November 2021; pp. 371–376. - DOI
-
- Rozaqi L., Nugroho A., Sanjaya K.H., Simbolon A.I. Design of Analog and Digital Filter of Electromyography; Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA); Serpong, Indonesia. 23–24 October 2019; New York, NY, USA: IEEE; pp. 186–192. - DOI
-
- Corvini G., D’Anna C., Conforto S. Estimation of mean and median frequency from synthetic sEMG signals: Effects of different spectral shapes and noise on estimation methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022;73:103420. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103420. - DOI
-
- Liu J., Zhang D., Sheng X., Zhu X. Quantification and solutions of arm movements effect on sEMG pattern recognition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2014;13:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014.05.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

