Reducing Noise, Artifacts and Interference in Single-Channel EMG Signals: A Review
- PMID: 36991639
- PMCID: PMC10059683
- DOI: 10.3390/s23062927
Reducing Noise, Artifacts and Interference in Single-Channel EMG Signals: A Review
Abstract
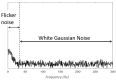
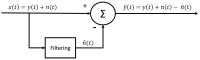
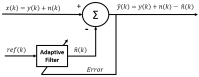
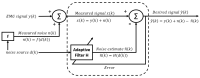
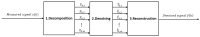
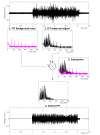
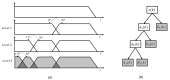
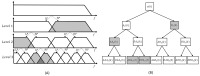
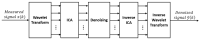
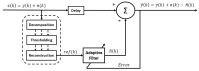
Electromyography (EMG) is gaining importance in many research and clinical applications, including muscle fatigue detection, control of robotic mechanisms and prostheses, clinical diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases and quantification of force. However, EMG signals can be contaminated by various types of noise, interference and artifacts, leading to potential data misinterpretation. Even assuming best practices, the acquired signal may still contain contaminants. The aim of this paper is to review methods employed to reduce the contamination of single channel EMG signals. Specifically, we focus on methods which enable a full reconstruction of the EMG signal without loss of information. This includes subtraction methods used in the time domain, denoising methods performed after the signal decomposition and hybrid approaches that combine multiple methods. Finally, this paper provides a discussion on the suitability of the individual methods based on the type of contaminant(s) present in the signal and the specific requirements of the application.
Keywords: artifact; contaminant reduction; denoising; electromyography; filtering; interference; noise; signal processing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chan B., Saad I., Bolong N., Siew K.E. A Review of Surface EMG in Clinical Rehabilitation Care Systems Design; Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 19th Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD); Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia. 23–25 November 2021; pp. 371–376. - DOI
-
- Rozaqi L., Nugroho A., Sanjaya K.H., Simbolon A.I. Design of Analog and Digital Filter of Electromyography; Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Sustainable Energy Engineering and Application (ICSEEA); Serpong, Indonesia. 23–24 October 2019; New York, NY, USA: IEEE; pp. 186–192. - DOI
-
- Corvini G., D’Anna C., Conforto S. Estimation of mean and median frequency from synthetic sEMG signals: Effects of different spectral shapes and noise on estimation methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022;73:103420. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103420. - DOI
-
- Liu J., Zhang D., Sheng X., Zhu X. Quantification and solutions of arm movements effect on sEMG pattern recognition. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2014;13:189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014.05.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

