Conformable Electrode Arrays for Wearable Neuroprostheses
- PMID: 36991692
- PMCID: PMC10054495
- DOI: 10.3390/s23062982
Conformable Electrode Arrays for Wearable Neuroprostheses
Abstract
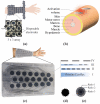
Wearable electrode arrays can selectively stimulate muscle groups by modulating their shape, size, and position over a targeted region. They can potentially revolutionize personalized rehabilitation by being noninvasive and allowing easy donning and doffing. Nevertheless, users should feel comfortable using such arrays, as they are typically worn for an extended time period. Additionally, to deliver safe and selective stimulation, these arrays must be tailored to a user's physiology. Fabricating customizable electrode arrays needs a rapid and economical technique that accommodates scalability. By leveraging a multilayer screen-printing technique, this study aims to develop personalizable electrode arrays by embedding conductive materials into silicone-based elastomers. Accordingly, the conductivity of a silicone-based elastomer was altered by adding carbonaceous material. The 1:8 and 1:9 weight ratio percentages of carbon black (CB) to elastomer achieved conductivities between 0.0021-0.0030 S cm-1 and were suitable for transcutaneous stimulation. Moreover, these ratios maintained their stimulation performance after several stretching cycles of up to 200%. Thus, a soft, conformable electrode array with a customizable design was demonstrated. Lastly, the efficacy of the proposed electrode arrays to stimulate hand function tasks was evaluated by in vivo experiments. The demonstration of such arrays encourages the realization of cost-effective, wearable stimulation systems for hand function restoration.
Keywords: carbon black; elastomer; electrode array; functional electrical stimulation; hand function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

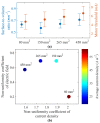

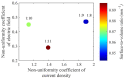
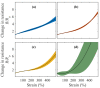

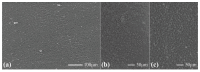
References
-
- Kenney L.P., Heller B.W., Barker A.T., Reeves M.L., Healey J., Good T.R., Cooper G., Sha N., Prenton S., Liu A., et al. A review of the design and clinical evaluation of the ShefStim array-based functional electrical stimulation system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016;38:1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2016.08.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

