Heterologous Prime-Boost Vaccination with Commercial FMD Vaccines Elicits a Broader Immune Response than Homologous Prime-Boost Vaccination in Pigs
- PMID: 36992134
- PMCID: PMC10058820
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11030551
Heterologous Prime-Boost Vaccination with Commercial FMD Vaccines Elicits a Broader Immune Response than Homologous Prime-Boost Vaccination in Pigs
Abstract
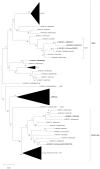
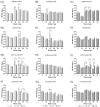
Three commercial vaccines are administered in domestic livestock farms for routine vaccination to aid for foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) control in Korea. Each vaccine contains distinct combinations of inactivated serotype O and A FMD virus (FMDV) antigens: O/Manisa + O/3039 + A/Iraq formulated in a double oil emulsion (DOE), O/Primorsky + A/Zabaikalsky formulated in a DOE, and O/Campos + A/Cruzeiro + A/2001 formulated in a single oil emulsion. Despite the recommendation for a prime-boost vaccination with the same vaccine in fattening pigs, occasional cross-inoculation is inevitable for many reasons, such as lack of compliance with vaccination guidelines, erroneous application, or change in vaccine types by suppliers. Therefore, there have been concerns that a poor immune response could be induced by cross-inoculation due to a failure to boost the immune response. In the present study, it was demonstrated by virus neutralization and ELISA tests that cross-inoculation of pigs with three commercial FMD vaccines does not hamper the immune response against the primary vaccine strains and enhances broader cross-reactivity against heterologous vaccine antigens whether they were applied or not. Therefore, it could be concluded that the cross-inoculation of FMD vaccines can be used as a regimen to strategically overcome the limitation of the antigenic spectrum induced by the original regimen.
Keywords: cross-inoculation; foot-and-mouth disease virus; heterologous prime-boost; homologous prime-boost; serological performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pereira H. Foot-and-mouth disease. In: Gibbs EPG, editor. Virus Diseases of Food Animals. Academic Press Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 1981. pp. 333–363.
-
- WOAH WOAH Terrestrial Manual Foot and Mouth Disease (Infection with Foot and Mouth Disease Virus) [(accessed on 11 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.01.08_FM....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

