Intraduodenal Delivery of Exosome-Loaded SARS-CoV-2 RBD mRNA Induces a Neutralizing Antibody Response in Mice
- PMID: 36992256
- PMCID: PMC10058540
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11030673
Intraduodenal Delivery of Exosome-Loaded SARS-CoV-2 RBD mRNA Induces a Neutralizing Antibody Response in Mice
Abstract
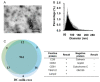
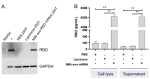
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has presented numerous challenges to global health. Vaccines, including lipid-based nanoparticle mRNA, inactivated virus, and recombined protein, have been used to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections in clinics and have been immensely helpful in controlling the pandemic. Here, we present and assess an oral mRNA vaccine based on bovine-milk-derived exosomes (milk-exos), which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) as an immunogen. The results indicate that RBD mRNA delivered by milk-derived exosomes can produce secreted RBD peptides in 293 cells in vitro and stimulates neutralizing antibodies against RBD in mice. These results indicate that SARS-CoV-2 RBD mRNA vaccine loading with bovine-milk-derived exosomes is an easy, cheap, and novel way to introduce immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in vivo. Additionally, it also can work as a new oral delivery system for mRNA.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; bovine-milk-derived exosomes; mRNA; neutralizing antibodies; oral vaccines; receptor-binding domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
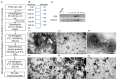
References
-
- Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., Shu H., Xia J., Liu H., Wu Y., Zhang L., Yu Z., Fang M., et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020;8:475–481. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lauer S.A., Grantz K.H., Bi Q., Jones F.K., Zheng Q., Meredith H.R., Azman A.S., Reich N.G., Lessler J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020;172:577–582. doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

