Tizoxanide Antiviral Activity on Dengue Virus Replication
- PMID: 36992406
- PMCID: PMC10055917
- DOI: 10.3390/v15030696
Tizoxanide Antiviral Activity on Dengue Virus Replication
Abstract
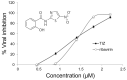
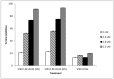
Dengue virus is an important circulating arbovirus in Brazil responsible for high morbidity and mortality worldwide, representing a huge economic and social burden, in addition to affecting public health. In this study, the biological activity, toxicity, and antiviral activity against dengue virus type 2 (DENV-2) of tizoxanide (TIZ) was evaluated in Vero cell culture. TIZ has a broad spectrum of action in inhibiting different pathogens, including bacteria, protozoa, and viruses. Cells were infected for 1 h with DENV-2 and then treated for 24 h with different concentrations of the drug. The quantification of viral production indicated the antiviral activity of TIZ. The protein profiles in infected Vero cells treated and not treated with TIZ were analyzed using the label-free quantitative proteomic approach. TIZ was able to inhibit virus replication mainly intracellularly after DENV-2 penetration and before the complete replication of the viral genome. Additionally, the study of the protein profile of infected not-treated and infected-treated Vero cells showed that TIZ interferes with cellular processes such as intracellular trafficking and vesicle-mediated transport and post-translational modifications when added after infection. Our results also point to the activation of immune response genes that would eventually lead to a decrease of DENV-2 production. TIZ is a promising therapeutic molecule for the treatment of DENV-2 infections.
Keywords: antiviral; dengue virus; tizoxanide; virucidal activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Racz M.L. Epidemiologia das infecções virais. In: Trabulsi L.R., Alterthum F., editors. Microbiologia. Atheneu; São Paulo, Brazil: 2008. pp. 573–576.
-
- Salles T.S., Sá-Guimarães T.D.E., De Alvarenga E.S.L., Guimarães-Ribeiro V., De Meneses M.D.F., De Castro-Salles P.F., Dos Santos C.R., Melo A.C.D.A., Soares M.R., Ferreira D.F., et al. History, epidemiology and diagnostics of dengue in the American and Brazilian contexts: A review. Parasit. Vectors. 2018;11:264. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2830-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

