Digital algorithm-guided insulin therapy in home healthcare for elderly persons with type 2 diabetes: A proof-of-concept study
- PMID: 36992745
- PMCID: PMC10012122
- DOI: 10.3389/fcdhc.2022.986672
Digital algorithm-guided insulin therapy in home healthcare for elderly persons with type 2 diabetes: A proof-of-concept study
Abstract
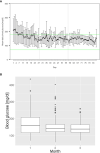
GlucoTab@MobileCare, a digital workflow and decision support system with integrated basal and basal-plus insulin algorithm was investigated for user acceptance, safety and efficacy in persons with type 2 diabetes receiving home health care by nurses. During a three months study nine participants (five female, age 77 ± 10 years, HbA1c 60 ± 13 mmol/mol (study start) vs. 57 ± 12 mmol/mol (study end) received basal or basal-plus insulin therapy as suggested by the digital system. In total 95% of all suggested tasks (blood glucose (BG) measurements, insulin dose calculations, insulin injections) were performed according to the digital system. Mean morning BG was 171 ± 68 mg/dL in the first study month vs. 145 ± 35 mg/dL in the last study month, indicating a reduced glycemic variability of 33 mg/dL (standard deviation). No hypoglycemic episode < 54 mg/dL occurred. User's adherence was high and the digital system supported a safe and effective treatment. Larger scale studies are needed to confirm findings under routine care.
German clinical trials register id: DRKS00015059.
Keywords: algorithm; digital; elderly; home healthcare; insulin therapy; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Kopanz, Mader, Donsa, Libiseller, Aberer, Pandis, Reinisch-Gratzer, Ambrosch, Lackner, Truskaller, Sinner, Pieber and Lichtenegger.
Conflict of interest statement
JM, FS, TP and KD are founders of the decide Clinical Software Ltd. JM is a member in the advisory board of Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Prediktor A/S, Roche Diabetes Care, Sanofi-Aventis and received speaker honoraria from Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, MSD, NovoNordisk A/S, Roche Diabetes Care, Sanofi, and Servier. FA received speaker honoraria from Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dome, Boehringer Ingelheim, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi Aventis, Amgen and travel grants from Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, Takeda, Merck Sharp & Dome and Amgen. TP is an advisory board member of Novo Nordisk A/S, consultant for Roche Diabetes Care, Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly & Co, Infineon, Carnegie Bank, shareholder of decide Clinical Software GmbH, and is on speaker’s bureau of Novo Nordisk A/S and Astra Zeneca. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: A patient-centered approach: position statement of the American diabetes association (ADA) and the European association for the study of diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care (2012) 35:1364–79. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0413 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources