Integrating Self-Management Education and Support in Routine Care of People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Conceptional Model Based on Critical Interpretive Synthesis and A Consensus-Building Participatory Consultation
- PMID: 36992783
- PMCID: PMC10012123
- DOI: 10.3389/fcdhc.2022.845547
Integrating Self-Management Education and Support in Routine Care of People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Conceptional Model Based on Critical Interpretive Synthesis and A Consensus-Building Participatory Consultation
Abstract
The integration of self-management education and support into the routine diabetes care is essential in preventing complications. Currently, however, there is no consensus on how to conceptualise integration in relation to self-management education and support. Therefore, this synthesis presents a framework conceptualising integration and self-management.
Methods: Seven electronic databases (Medline, HMIC, PsycINFO, CINAHL, ERIC, Scopus and Web of Science) were searched. Twenty-one articles met the inclusion criteria. Data were synthesised using principles of critical interpretive synthesis to build the conceptual framework. The framework was presented to 49 diabetes specialist nurses working at different levels of care during a multilingual workshop.
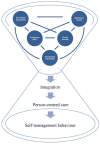
Results: A conceptual framework is proposed in which integration is influenced by five interacting components: the programme ethos of the diabetes self-management education and support intervention (content and delivery), care system organisation (the framework in which such interventions are delivered), adapting to context (the aspects of the people receiving and delivering the interventions), interpersonal relationship (the interactions between the deliverer and receiver of the intervention), and shared learning (what deliverer and receiver gain from the interactions). The critical inputs from the workshop participants related to the different priorities given to the components according to their sociolinguistic and educational experiences, Overall, they agreed with the conceptualisation of the components and their content specific to diabetes self-management education and support.
Discussion: Integration was conceptualised in terms of the relational, ethical, learning, contextual adapting, and systemic organisational aspects of the intervention. It remains uncertain which prioritised interactions of components and to what extent these may moderate the integration of self-management education and support into routine care; in turn, the level of integration observed in each of the components may moderate the impact of these interventions, which may also apply to the impact of the professional training.
Conclusion: This synthesis provides a theoretical framework that conceptualises integration in the context of diabetes self-management education and support in routine care. More research is required to evaluate how the components identified in the framework can be addressed in clinical practice to assess whether improvements in self-management education and support can be effectively realised in this population.
Keywords: complex adaptive systems; critical interpretive synthesis; integration; self-management education and support; theory development; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Huber, Montreuil, Christie and Forbes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes. Clin Diabetes (2011) 29(3):116–22. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.29.3.116 - DOI
-
- Kassebaum NJ, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown J, Carter A, et al. Global, Regional, and National Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs) for 315 Diseases and Injuries and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE), 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet (2016) 388(10053):1603–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31460-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prattichizzo F, de Candia P, De Nigris V, Nicolucci A, Ceriello A. Legacy Effect of Intensive Glucose Control on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Trials According to Different Scenarios. Metabolism (2020) 110:154308. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154308 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous