Enhancing safe motherhood: Effect of novel partograph on labor outcomes and its utility: An Indian perspective
- PMID: 36993003
- PMCID: PMC10041330
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1326_22
Enhancing safe motherhood: Effect of novel partograph on labor outcomes and its utility: An Indian perspective
Abstract
Introduction: Safe motherhood ensures safe pregnancy and childbirth. One of the noteworthy causes of maternal morbidity and mortality is the complications arising from prolonged or obstructed labour. World Health Organization recommends the use of partograph to significantly reduce the maternal mortality crisis. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a novel partograph in terms of maternal and perinatal outcomes along with its utility.
Materials and methods: A total of 400 intranatal women were selected in a non-randomized control trial to evaluate the effectiveness of novel partograph on selected maternal and perinatal outcomes. Subjects in experimental group (n=200) received care with newly developed partograph whereas subjects in control group (n=200) received standard care. Effectiveness was determined at a significance level of α ≤ 0.05. Utility of the novel partograph was determined as perceived by nurses.
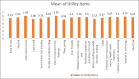
Results: There was significant reduction in the duration of the 1st and 2nd stage of labour (P=0.023 and 0.006 respectively) and number of vaginal examinations performed during labour (P=0.017) among mothers in the experimental group. Significant improvement in the Apgar score (P=0.005) was also observed among the infants of mothers in experimental group. Novel partograph was considered as of having extreme utility by 71% nurses.
Conclusion: Study concluded that subjects monitored by the partograph experienced improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. It was found to be having extreme utility.
Keywords: India; labor; maternal outcome; partograph; perinatal outcome.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of partograph use on outcomes for women in spontaneous labour at term and their babies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 6;8(8):CD005461. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005461.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30080256 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of the modified WHO labour care guide to detect prolonged and obstructed labour among women admitted at publicly funded facilities in rural Mbarara district, Southwestern Uganda: an ambispective cohort study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 5:2024.09.04.24313073. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.24313073. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Int J Womens Health. 2025 Feb 04;17:271-285. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S498903. PMID: 39281732 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Effectiveness of the Modified WHO Labour Care Guide to Detect Prolonged and Obstructed Labour Among Women Admitted at Eight Publicly Funded, Midwife-Led Community Health Facilities in Rural Mbarara District, Southwestern Uganda: An Ambispective Cohort Study.Int J Womens Health. 2025 Feb 4;17:271-285. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S498903. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 39925783 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Completion of the modified World Health Organization (WHO) partograph during labour in public health institutions of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.Reprod Health. 2013 Apr 18;10:23. doi: 10.1186/1742-4755-10-23. Reprod Health. 2013. PMID: 23597239 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of Partograph for Labor Management Among Healthcare Providers in Healthcare Facilities in India: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Aug 28;15(8):e44242. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44242. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37772204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a novel labour monitoring tool: Improving labour care quality in the Indian setting.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Mar;13(3):869-874. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_862_23. Epub 2024 Apr 4. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38736837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manglik PG. Safe motherhood day:Challenges in fostering safe motherhood in India and way forward:Times of India. [Last accessed on 2022 May 25];2022 April; Available from:https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/voices/safe-motherhood-day-cha...
-
- World Health Organization. [Last accessed on 2021 May 19];Maternal mortality. 2019 Available from:https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality .
-
- [Last accessed on 2020 Jan 20];NHM. Guidelines of maternal death and surveillance and response. 2017 Available from:https://nhm.gov.in/images/pdf/programmes/maternal-health/guidelines/Guid... .
-
- Alkema L, Chou D, Hogan D, Zhang S, Moller AB, Gemmill A, et al. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in maternal mortality between 1990 and 2015, with scenario-based projections to 2030:A systematic analysis by the UN Maternal Mortality Estimation Inter-Agency Group. Lancet. 2016;387:462–74. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources