Kounis syndrome and atrial fibrillation after bee sting: A case report
- PMID: 36993105
- PMCID: PMC10041273
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_901_22
Kounis syndrome and atrial fibrillation after bee sting: A case report
Abstract
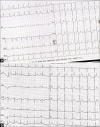
Bee sting can lead to allergic reactions which can present as life-threatening emergencies. Kounis syndrome is an acute coronary syndrome caused by mast cell activation after exposure to an allergen. Atrial fibrillation (AF) along with Kounis syndrome after allergen exposure is a rare presentation. A 40-year-old male patient presented to the emergency department (ED) with multiple bee stings to the face and neck. He complained of retrosternal chest pain along with facial pain and swelling. An electrocardiogram (ECG) showed AF with ST elevation in aVR and generalized ST segment depression. Troponin levels were elevated. He was diagnosed with Kounis syndrome along with AF secondary to a bee sting. The patient improved symptomatically with removal of stings and conservative management (steroids, antihistamines, antiplatelet drugs). ECG reverted to sinus rhythm and resolution of ST-T changes. He was discharged from the ED in stable condition. The bee sting may lead to significant cardiovascular events such as AF and Kounis syndrome, which require a high index of suspicion and prompt treatment. Kounis syndrome should be suspected in the ED in young patients with no cardiovascular risk factors after exposure to an allergen.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Kounis syndrome; bee sting.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kounis Syndrome: Bee Sting-Induced Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cureus. 2023 Oct 23;15(10):e47507. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47507. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021736 Free PMC article.
-
Different types of Kounis syndrome caused by different episodes of bee sting anaphylaxis: Misfortunes never come singly.J Cardiol Cases. 2022 Mar 26;26(1):81-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2022.03.002. eCollection 2022 Jul. J Cardiol Cases. 2022. PMID: 35923521 Free PMC article.
-
Kounis syndrome caused by bee sting: a case report and literature review.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2023 Sep-Oct 23;34(4):256-259. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2022-042. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2023. PMID: 36044199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kounis Syndrome after Oral Amoxicillin Clavulanate.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2025 Jan-Mar;15(1):66-68. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_461_24. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40336762 Free PMC article.
-
A case of Kounis syndrome after a hornet sting and literature review.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Dec 3;7:867. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-867. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25465208 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical complications in envenoming by Apis honeybee stings: insights into mechanisms, diagnosis, and pharmacological interventions.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 18;15:1437413. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437413. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39359723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kounis Syndrome: Bee Sting-Induced Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cureus. 2023 Oct 23;15(10):e47507. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47507. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021736 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of human envenoming by terrestrial venomous animals: Routine, advances, and perspectives.Toxicon X. 2024 Oct 10;24:100211. doi: 10.1016/j.toxcx.2024.100211. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicon X. 2024. PMID: 39507426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kadeli D, Mangesh D, Keshava R, Gopi A. Kounis syndrome:Allergic myocardial infarction!! J Indian Coll Cardiol. 2019;9:108.
-
- Sahinkus S, Demirel S. 74.eestings and a review of. Atrial fibrillation due to bee sting. J Clin Toxicol. 2017;7:361.
-
- Kounis NG. Coronary hypersensitivity disorder:The Kounis syndrome. Clin Ther. 2013;35:563–71. - PubMed
-
- Kounis NG. Kounis syndrome (allergic angina and allergic myocardial infarction):A natural paradigm? Int J Cardiol. 2006;110:7–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials