This is a preprint.
Immune niches in brain metastases contain TCF1+ stem-like T cells, are associated with disease control and are modulated by preoperative SRS
- PMID: 36993444
- PMCID: PMC10055679
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2722744/v1
Immune niches in brain metastases contain TCF1+ stem-like T cells, are associated with disease control and are modulated by preoperative SRS
Update in
-
Pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery and peri-operative dexamethasone for resectable brain metastases: a two-arm pilot study evaluating clinical outcomes and immunological correlates.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 14;15(1):8854. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53034-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39402027 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Abstract
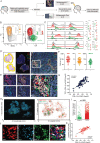
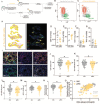
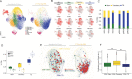
The CD8+ T-cell response is prognostic for survival outcomes in several tumor types. However, whether this extends to tumors in the brain, an organ with barriers to T cell entry, remains unclear. Here, we analyzed immune infiltration in 67 brain metastasis (BrM) and found high frequencies of PD1+ TCF1+ stem-like CD8+ T-cells and TCF1- effector-like cells. Importantly, the stem-like cells aggregate with antigen presenting cells in immune niches, and niches were prognostic for local disease control. Standard of care for BrM is resection followed by stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), so to determine SRS's impact on the BrM immune response, we examined 76 BrM treated with pre-operative SRS (pSRS). pSRS acutely reduced CD8+ T cells at 3 days. However, CD8+ T cells rebounded by day 6, driven by increased frequency of effector-like cells. This suggests that the immune response in BrM can be regenerated rapidly, likely by the local TCF1+ stem-like population.
Figures


References
-
- Naito Y. et al. CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58, 3491–3494 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

