Generation of new rice germplasms with low amylose content by CRISPR/CAS9-targeted mutagenesis of the FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2 gene
- PMID: 36993856
- PMCID: PMC10040805
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1138523
Generation of new rice germplasms with low amylose content by CRISPR/CAS9-targeted mutagenesis of the FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2 gene
Abstract
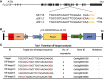
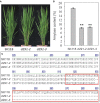
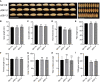
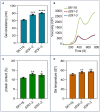
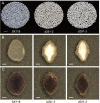
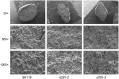
FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2 (FLO2), encoding a tetratricopeptide repeat domain (TPR)-containing protein located in the nucleus, is considered to be a regulatory protein that controls the biosynthesis of seed storage substances. The diversity of flo2 allele is attributable for the variations in grain appearance, amylose content (AC), and physicochemical properties, influencing the eating and cooking quality (ECQ) of rice. In this study, we used CRISPR/Cas9 to introduce loss-of-function mutations into the FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2 gene in Suken118 (SK118), a widely cultivated elite japonica rice variety in Jiangsu, China. Physiochemical analyses of the flo2 mutants were congruent with previous studies, exhibiting lowered AC and viscosity, risen gel consistency (GC) and gelatinization temperature (GT) values, which were all instrumental to the improvement of ECQ. However, the wrinkled opaque appearance and the decrease in grain width, grain thickness and grain weight imply trade-offs in grain yield. Despite the ex-ante estimation for low yielding, the superior ECQ in these novel genotypes generated by using genome editing approach may have the potential for formulating high value specialty food.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; FLOURY ENDOSPERM 2; amylose content (AC); eating and cooking quality (ECQ); genome editing; japonica rice.
Copyright © 2023 Song, Chen, Du, Li, Fei, Tao, Wang, Xu, Li, Wang, Liang, Zhou, Tan, Li and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three novel alleles of FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 (FLO2) confer dull grains with low amylose content in rice.Plant Sci. 2015 Apr;233:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25711812
-
Improving rice eating and cooking quality by coordinated expression of the major starch synthesis-related genes, SSII and Wx, in endosperm.Plant Mol Biol. 2021 Jul;106(4-5):419-432. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01162-8. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Plant Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34129189
-
A novel factor FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 is involved in regulation of rice grain size and starch quality.Plant Cell. 2010 Oct;22(10):3280-94. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.070821. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20889913 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Deletion of the First Intron of the Wxb Allele via CRISPR/Cas9 Significantly Increases Grain Amylose Content in Rice.Rice (N Y). 2022 Jan 4;15(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12284-021-00548-y. Rice (N Y). 2022. PMID: 34982277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes and Their Molecular Functions Determining Seed Structure, Components, and Quality of Rice.Rice (N Y). 2022 Mar 18;15(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12284-022-00562-8. Rice (N Y). 2022. PMID: 35303197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9: a sustainable technology to enhance climate resilience in major Staple Crops.Front Genome Ed. 2025 Mar 18;7:1533197. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2025.1533197. eCollection 2025. Front Genome Ed. 2025. PMID: 40171546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas Technology Revolutionizes Crop Breeding.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;12(17):3119. doi: 10.3390/plants12173119. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TaMIR397-6A and -6B Homoeologs Encode Active miR397 Contributing to the Regulation of Grain Size in Hexaploid Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 13;25(14):7696. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147696. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao S., Yicong C., Baobing F., Guiai J., Zhonghua S., Ju L., et al. . (2019). Editing of rice isoamylase gene ISA1 provides insights into its function in starch formation. Rice Sci. 26 (2), 77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.07.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

