Assessment of knowledge of ASHA workers regarding MCH services and practices followed by mothers - A field study
- PMID: 36994002
- PMCID: PMC10041030
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_812_22
Assessment of knowledge of ASHA workers regarding MCH services and practices followed by mothers - A field study
Abstract
Background: Accredited social health activist (ASHA) workers act as a "bridge" between rural people and health service outlets and play a central role in achieving national health and population policy goals. According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) V (2019-2021) data, infant mortality rate (IMR) is still high in rural areas (32.4 per 1000 live births) in Punjab, compared to urban areas (20.1). Maternal mortality ratio (MMR) is also high (129 per lakh), according to sample registration system (SRS) 2016-2018 data.
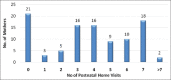
Materials and methods: In this descriptive, cross-sectional study conducted at RHTC, Bhadson, we assessed the knowledge of ASHA workers regarding maternal and child health (MCH) services and their provision by them to their beneficiaries (mothers with children aged 0-6 months). Out of the total 196 ASHA workers, 72 were selected randomly to assess their knowledge, while 100 beneficiary mothers were interviewed face to face to assess the services provided by the ASHA workers.
Results: Almost 65.2% of ASHA workers were above 35 years of age. Majority of the ASHA workers (40/72) replied that average weight gain in pregnancy is 10 kg. Very few, that is, 17 (23.6%), ASHA workers knew that breastfeeding should be started within the first hour after delivery of the baby. Counseling regarding nutrition, birth preparedness, institutional delivery, and birth registration was given by ASHA workers to 75%-85% of mothers. There was statistically significant improvement in the practices by mothers with the counseling given by ASHA workers regarding pre-lacteal feed, utilization of family planning methods, and delaying early bathing.
Conclusions: The study concludes that ASHA workers have good knowledge regarding various aspects of antenatal period, but when it comes to postnatal period and care of the newborn, there are some lacunae. These aspects of newborn care need to be reinforced into the refresher trainings of the ASHA workers.
Keywords: ASHA workers; MCH services; rural health training center.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Park K. Health programmes in India. In: Park K, editor. Park's Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. 23rd ed. Jabalpur: M/s Banarsidas Bhanot Publishers; 2015. pp. 432–503.
-
- Garg PK, Bhardwaj A, Singh A, Ahluwalia SK. An evaluation of ASHA worker's awareness and practice of their responsibilities in rural Haryana. Natl J Community Med. 2013;4:76–80.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources