Evaluation of 6-OxP-CD, an Oxime-based cyclodextrin as a viable medical countermeasure against nerve agent poisoning: Experimental and molecular dynamic simulation studies on its inclusion complexes with cyclosarin, soman and VX
- PMID: 36996021
- PMCID: PMC10062596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283181
Evaluation of 6-OxP-CD, an Oxime-based cyclodextrin as a viable medical countermeasure against nerve agent poisoning: Experimental and molecular dynamic simulation studies on its inclusion complexes with cyclosarin, soman and VX
Abstract
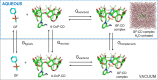
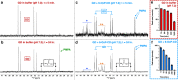
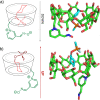
The ability of the cyclodextrin-oxime construct 6-OxP-CD to bind and degrade the nerve agents Cyclosarin (GF), Soman (GD) and S-[2-[Di(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl] O-ethyl methylphosphonothioate (VX) has been studied using 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) under physiological conditions. While 6-OxP-CD was found to degrade GF instantaneously under these conditions, it was found to form an inclusion complex with GD and significantly improve its degradation (t1/2 ~ 2 hrs) relative over background (t1/2 ~ 22 hrs). Consequently, effective formation of the 6-OxP-CD:GD inclusion complex results in the immediate neutralization of GD and thus preventing it from inhibiting its biological target. In contrast, NMR experiments did not find evidence for an inclusion complex between 6-OxP-CD and VX, and the agent's degradation profile was identical to that of background degradation (t1/2 ~ 24 hrs). As a complement to this experimental work, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations coupled with Molecular Mechanics-Generalized Born Surface Area (MM-GBSA) calculations have been applied to the study of inclusion complexes between 6-OxP-CD and the three nerve agents. These studies provide data that informs the understanding of the different degradative interactions exhibited by 6-OxP-CD with each nerve agent as it is introduced in the CD cavity in two different orientations (up and down). For its complex with GF, it was found that the oxime in 6-OxP-CD lies in very close proximity (PGF⋯OOxime ~ 4-5 Å) to the phosphorus center of GF in the 'downGF' orientation for most of the simulation accurately describing the ability of 6-OxP-CD to degrade this nerve agent rapidly and efficiently. Further computational studies involving the center of masses (COMs) for both components (GF and 6-OxP-CD) also provided some insight on the nature of this inclusion complex. Distances between the COMs (ΔCOM) lie closer in space in the 'downGF' orientation than in the 'upGF' orientation; a correlation that seems to hold true not only for GF but also for its congener, GD. In the case of GD, calculations for the 'downGD' orientation showed that the oxime functional group in 6-OxP-CD although lying in close proximity (PGD⋯OOxime ~ 4-5 Å) to the phosphorus center of the nerve agent for most of the simulation, adopts another stable conformation that increase this distance to ~ 12-14 Å, thus explaining the ability of 6-OxP-CD to bind and degrade GD but with less efficiency as observed experimentally (t1/2 ~ 4 hr. vs. immediate). Lastly, studies on the VX:6-OxP-CD system demonstrated that VX does not form a stable inclusion complex with the oxime-bearing cyclodextrin and as such does not interact in a way that is conducive to an accelerated degradation scenario. Collectively, these studies serve as a basic platform from which the development of new cyclodextrin scaffolds based on 6-OxP-CD can be designed in the development of medical countermeasures against these highly toxic chemical warfare agents.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Howes L. Novichok compound poisoned Navalny. Chem Eng News 2020;98:5.
-
- Haines DD, Fox SC. Acute and Long-Term Impact of Chemical Weapons: Lessons from the Iran-Iraq War. Forensic Sci Rev. 2014;26(2),97–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials