Blood transcriptome of Rasa Aragonesa rams with different sexual behavior phenotype reveals CRYL1 and SORCS2 as genes associated with this trait
- PMID: 36996265
- PMCID: PMC10118393
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/skad098
Blood transcriptome of Rasa Aragonesa rams with different sexual behavior phenotype reveals CRYL1 and SORCS2 as genes associated with this trait
Abstract
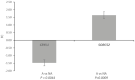
Reproductive fitness of rams is seasonal, showing the highest libido during short days coinciding with the ovarian cyclicity resumption in the ewe. However, the remarkable variation in sexual behavior between rams impair farm efficiency and profitability. Intending to identify in vivo sexual behavior biomarkers that may aid farmers to select active rams, transcriptome profiling of blood was carried out by analyzing samples from 6 sexually active (A) and 6 nonactive (NA) Rasa Aragonesa rams using RNA-Seq technique. A total of 14,078 genes were expressed in blood but only four genes were differentially expressed (FDR < 0.10) in the A vs. NA rams comparison. The genes, acrosin inhibitor 1 (ENSOARG00020023278) and SORCS2, were upregulated (log2FC > 1) in active rams, whereas the CRYL1 and immunoglobulin lambda-1 light chain isoform X47 (ENSOARG00020025518) genes were downregulated (log2FC < -1) in this same group. Gene set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) identified 428 signaling pathways, predominantly related to biological processes. The lysosome pathway (GO:0005764) was the most enriched, and may affect fertility and sexual behavior, given the crucial role played by lysosomes in steroidogenesis, being the SORCS2 gene related to this signaling pathway. Furthermore, the enriched positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade (GO:0070374) pathway is associated with reproductive phenotypes such as fertility via modulation of hypothalamic regulation and GnRH-mediated production of pituitary gonadotropins. Furthermore, external side of plasma membrane (GO:0009897), fibrillar center (GO:0001650), focal adhesion (GO:0005925), and lamellipodium (GO:0030027) pathways were also enriched, suggesting that some molecules of these pathways might also be involved in rams' sexual behavior. These results provide new clues for understanding the molecular regulation of sexual behavior in rams. Further investigations will be needed to confirm the functions of SORCS2 and CRYL1 in relation to sexual behavior.
Keywords: CRYL1; SORCS2; blood; rams; sexual behavior; transcriptome.
Plain language summary
Analyzing ram sexual behavior via blood transcriptome profiling can help to identify in vivo sexual behavior biomarkers as an innovative alternative to invasive and time-consuming methods in farms. Using RNA-sequencing technique, we compared 12 Rasa Aragonesa rams with different sexual behavior (6 sexually active and 6 nonactive) to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in peripheral blood putatively responsible of libido differences between rams. Comparative analysis revealed four candidate genes and several signaling pathways related to sexual behavior such as lysosome, and positive regulation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1 and ERK2) cascade. This data will be helpful for further investigations to understand the differences of sheep sexual behavior.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring differentially expressed genes in hypothalamic, pars tuberalis and pineal gland transcriptomes in different sexual behavior phenotypes in rams using RNA-Seq.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skac365. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac365. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36331073 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms of the melatonin receptor 1A (MTNR1A) gene influence the age at first mating in autumn-born ram-lambs and sexual activity of adult rams in spring.Theriogenology. 2020 Nov;157:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.07.030. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Theriogenology. 2020. PMID: 32799126
-
Ram mating behavior after long-term selection for reproductive rate in Rambouillet ewes.J Anim Sci. 2002 Oct;80(10):2588-93. J Anim Sci. 2002. PMID: 12413080
-
The ram as a model for behavioral neuroendocrinology.Horm Behav. 2007 Jun;52(1):70-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.03.016. Epub 2007 Mar 31. Horm Behav. 2007. PMID: 17482616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual partner preference, hypothalamic morphology and aromatase in rams.Physiol Behav. 2004 Nov 15;83(2):233-45. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.08.017. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15488542 Review.
Cited by
-
Four Markers Useful for the Distinction of Intrauterine Growth Restriction in Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;13(21):3305. doi: 10.3390/ani13213305. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958061 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Runs of Homozygosity Reveal Inbreeding Levels and Trait-Associated Candidate Genes in Diverse Sheep Breeds.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;16(3):316. doi: 10.3390/genes16030316. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149467 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of Runs of Homozygosity Distribution Patterns and Relevant Candidate Genes of Potential Economic Interest in Russian Goat Breeds Using Whole-Genome Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2025 May 24;16(6):631. doi: 10.3390/genes16060631. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, B. M., Cockett N. E., Burton D. J., Hadfield T. L., and Moss G. E.. . 2012. Reproductive performance of rams in three producer range flocks: evidence of poor sexual behavior in the field. Small Rumin. Res. 107:117–120. doi:10.1016/J.SMALLRUMRES.2012.04.003. - DOI
-
- Almeida, S., Miranda A. M., Tóth A. E., Nielsen M. S., and Oliveira T. G.. . 2021. SorCS2 deletion leads to altered neuronal lysosome activity. BioRxiv doi:10.1101/2021.04.08.439000. - DOI
-
- Andersen, C. L., Jensen J. L., and Ørntoft T. F.. . 2004. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrews, S. 2015. FastQC. A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.Babraham Inst.1:1. https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=95c0b572-b20b-45da-b380-4227fc7...
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

