Measurable Residual Disease and Fusion Partner Independently Predict Survival and Relapse Risk in Childhood KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group
- PMID: 36996387
- PMCID: PMC10414713
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.02120
Measurable Residual Disease and Fusion Partner Independently Predict Survival and Relapse Risk in Childhood KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group
Abstract
Purpose: A previous study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group (I-BFM-SG) on childhood KMT2A-rearranged (KMT2A-r) AML demonstrated the prognostic value of the fusion partner. This I-BFM-SG study investigated the value of flow cytometry-based measurable residual disease (flow-MRD) and evaluated the benefit of allogeneic stem-cell transplantation (allo-SCT) in first complete remission (CR1) in this disease.
Methods: A total of 1,130 children with KMT2A-r AML, diagnosed between January 2005 and December 2016, were assigned to high-risk (n = 402; 35.6%) or non-high-risk (n = 728; 64.4%) fusion partner-based groups. Flow-MRD levels at both end of induction 1 (EOI1) and 2 (EOI2) were available for 456 patients and were considered negative (<0.1%) or positive (≥0.1%). End points were 5-year event-free survival (EFS), cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR), and overall survival (OS).
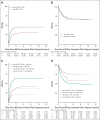
Results: The high-risk group had inferior EFS (30.3% high risk v 54.0% non-high risk; P < .0001), CIR (59.7% v 35.2%; P < .0001), and OS (49.2% v 70.5%; P < .0001). EOI2 MRD negativity was associated with superior EFS (n = 413; 47.6% MRD negativity v n = 43; 16.3% MRD positivity; P < .0001) and OS (n = 413; 66.0% v n = 43; 27.9%; P < .0001), and showed a trend toward lower CIR (n = 392; 46.1% v n = 26; 65.4%; P = .016). Similar results were obtained for patients with EOI2 MRD negativity within both risk groups, except that within the non-high-risk group, CIR was comparable with that of patients with EOI2 MRD positivity. Allo-SCT in CR1 only reduced CIR (hazard ratio, 0.5 [95% CI, 0.4 to 0.8]; P = .00096) within the high-risk group but did not improve OS. In multivariable analyses, EOI2 MRD positivity and high-risk group were independently associated with inferior EFS, CIR, and OS.
Conclusion: EOI2 flow-MRD is an independent prognostic factor and should be included as risk stratification factor in childhood KMT2A-r AML. Treatment approaches other than allo-SCT in CR1 are needed to improve prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Prognostic importance of the fusion partners and measurable residual disease in patients with acute myeloid leukemia who harbor 11q23/KMT2A alterations.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Oct 30;12(10):1920-1925. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-360. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37969120 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fusion and flow: refining risk prediction in KMT2A-rearranged pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Dec 26;12(12):2099-2102. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-436. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 38197101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Creutzig U, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Gibson B, et al. : Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in children and adolescents: Recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 120:3187-3205, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Segerink WH, de Haas V, Kaspers GJL: Measurable residual disease in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 21:451-459, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Buldini B, Rizzati F, Masetti R, et al. : Prognostic significance of flow-cytometry evaluation of minimal residual disease in children with acute myeloid leukaemia treated according to the AIEOP-AML 2002/01 study protocol. Br J Haematol 177:116-126, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

