Mucins as contrast agent targets for fluorescence-guided surgery of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 36997106
- PMCID: PMC10150776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216150
Mucins as contrast agent targets for fluorescence-guided surgery of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
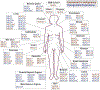
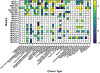
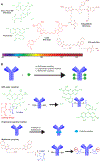
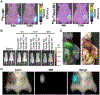
Pancreatic cancer is difficult to resect due to its unique challenges, often leading to incomplete tumor resections. Fluorescence-guided surgery (FGS), also known as intraoperative molecular imaging and optical surgical navigation, is an intraoperative tool that can aid surgeons in complete tumor resection through an increased ability to detect the tumor. To target the tumor, FGS contrast agents rely on biomarkers aberrantly expressed in malignant tissue compared to normal tissue. These biomarkers allow clinicians to identify the tumor and its stage before surgical resection and provide a contrast agent target for intraoperative imaging. Mucins, a family of glycoproteins, are upregulated in malignant tissue compared to normal tissue. Therefore, these proteins may serve as biomarkers for surgical resection. Intraoperative imaging of mucin expression in pancreatic cancer can potentially increase the number of complete resections. While some mucins have been studied for FGS, the potential ability to function as a biomarker target extends to the entire mucin family. Therefore, mucins are attractive proteins to investigate more broadly as FGS biomarkers. This review summarizes the biomarker traits of mucins and their potential use in FGS for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Fluorescence; Intraoperative molecular imaging; Mucins; Optical surgical navigation.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Kathryn M. Muilenburg: None. Carly C. Isder: None. Prakash Radhakrishnan: Equity interest in OncoCare Therapeutics, which has licensing rights to antibody AR9.6. NIH funding related mucins. Surinder K. Batra: Co-founders of Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Inc., Omaha. Recipient of NIH funding related to mucins and fluorescence-guided surgery contrast agents that target mucins. Quan P. Ly: Co-investigator of NIH funding related pancreatic cancer and fluorescence-guided surgery. Stock ownership in Intuitive Surgical. Other stock information available upon request. Mark A. Carlson: Recent NIH funding related to fluorescence-guided surgery. Michael Bouvet: Consultant for Stryker, Inc. NIH and VA funding related anti-mucin antibodies for fluorescence-guided surgery. Michael A. Hollingsworth: Equity interest in OncoCare Therapeutics and Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Recipient of NIH funding related to mucins and biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. Aaron M. Mohs: NIH funding related to fluorescence-guided surgery targeting mucins. Patents related to contrast agents and imaging systems for fluorescence-guided surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Borrebaeck CA, Precision diagnostics: moving towards protein biomarker signatures of clinical utility in cancer, Nat Rev Cancer, 17 (2017) 199–204. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A, Creek DJ, Discovery and Validation of Clinical Biomarkers of Cancer: A Review Combining Metabolomics and Proteomics, Proteomics, 19 (2019) e1700448. - PubMed

