Respiratory brain impulse propagation in focal epilepsy
- PMID: 36997658
- PMCID: PMC10063583
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32271-7
Respiratory brain impulse propagation in focal epilepsy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Respiratory brain impulse propagation in focal epilepsy.Sci Rep. 2023 May 9;13(1):7515. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34268-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37160935 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
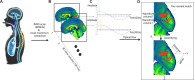
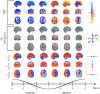
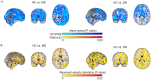
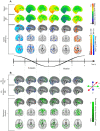
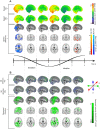
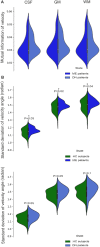
Respiratory brain pulsations pertaining to intra-axial hydrodynamic solute transport are markedly altered in focal epilepsy. We used optical flow analysis of ultra-fast functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data to investigate the velocity characteristics of respiratory brain impulse propagation in patients with focal epilepsy treated with antiseizure medication (ASM) (medicated patients with focal epilepsy; ME, n = 23), drug-naïve patients with at least one seizure (DN, n = 19) and matched healthy control subjects (HC, n = 75). We detected in the two patient groups (ME and DN) several significant alterations in the respiratory brain pulsation propagation velocity, which showed a bidirectional change dominated by a reduction in speed. Furthermore, the respiratory impulses moved more in reversed or incoherent directions in both patient groups vs. the HC group. The speed reductions and directionality changes occurred in specific phases of the respiratory cycle. In conclusion, irrespective of medication status, both patient groups showed incoherent and slower respiratory brain impulses, which may contribute to epileptic brain pathology by hindering brain hydrodynamics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lach P, et al. Neuroinflammation in epilepsy—Diagnostics and therapeutic perspectives. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022;8:31–35. doi: 10.1007/s40495-021-00270-9. - DOI

