Lactococcus lactis endocarditis and liver abscess in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 36997999
- PMCID: PMC10064683
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-022-03676-1
Lactococcus lactis endocarditis and liver abscess in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Over the last two decades, several cases of infections caused by Lactococcus lactis have been reported. This Gram-positive coccus is considered non-pathogenic for humans. However, in some rare cases, it can cause serious infections such as endocarditis, peritonitis, and intra-abdominal infections.
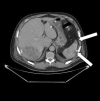
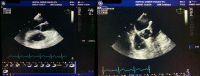
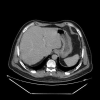
Case presentation: A 56-year-old Moroccan patient was admitted to the hospital because of diffuse abdominal pain and fever. The patient had no past medical history. Five days before his admission, he developed abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant along with chills and feverish sensations. Investigations showed a liver abscess, which was drained, and the microbiological study of the pus revealed Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. Three days after admission, control computed tomography objectified splenic infarctions. Cardiac explorations were performed and showed a floating vegetation on the ventricle side of the aortic valve. We retained the diagnosis of infectious endocarditis according to the modified Duke criteria. The patient was declared afebrile on day 5 and the evolution was clinically and biologically favorable. Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, formerly known as Streptococcus cremoris, is a rare cause of human infections. The first case of Lactococcus lactis cremoris endocarditis was reported in 1955. This organism includes three subspecies: lactis, cremoris, and hordniae. A MEDLINE and Scopus search showed only 13 cases of infectious endocarditis due to Lactococcus lactis, with subsp. cremoris identified in four of the cases.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first case report of the co-occurrence of Lactococcus lactis endocarditis and liver abscess. Despite its reported low virulence and good response to antibiotic treatment, Lactococcus lactis endocarditis must be considered a serious disease. It is imperative for a clinician to suspect this microorganism of causing endocarditis when they notice signs of infectious endocarditis in a patient with a history of consumption of unpasteurized dairy products or contact with farm animals. The finding of a liver abscess should lead to an investigation of endocarditis, even in previously healthy patients without obvious clinical signs of endocarditis.
Keywords: Endocarditis; Lactococcus lactis; Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris; Liver abscess; Splenic infarction.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Liver abscess and empyema due to Lactococcus lactis cremoris.J Korean Med Sci. 2010 Nov;25(11):1669-71. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.11.1669. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21060760 Free PMC article.
-
Infective endocarditis caused by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and Pediococcus pentosaceus: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(50):e13658. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013658. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30558065 Free PMC article.
-
Brain abscess caused by Lactococcus lactis cremoris in a child.Eur J Pediatr. 2011 Dec;170(12):1603-5. doi: 10.1007/s00431-011-1586-3. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Eur J Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21953033
-
Subdural empyema due to Lactococcus lactis cremoris: case report.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(4):341-7. doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr2012-0440. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014. PMID: 24257498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactococcus lactis cholangitis and bacteremia identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: A case report and review of the literature on Lactococcus lactis infection.J Infect Chemother. 2019 Feb;25(2):141-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2018.07.010. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Infect Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30100399 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of the intestinal microbiome in Rattus norvegicus from different geographies.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 3;14:1283453. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1283453. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029126 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, Characterization, and Epidemiological Analysis of Lactococcus garvieae Fish Isolates Obtained in a Period of Eighteen Years.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 17;13(2):436. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020436. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005801 Free PMC article.
-
A "fishy" situation, rare pathogen and presentation in prosthetic valve infective endocarditis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 4;10(11):e32383. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32383. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38933970 Free PMC article.
-
Functional genomic insights into Floricoccus penangensis ML061-4 isolated from leaf surface of Assam tea.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):2951. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86602-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39848972 Free PMC article.
-
Application of PCR-Based Techniques for the Identification of Genetic Fingerprint Diversity of Dominant Bacteria in Fecal Samples of Children with Diarrhea in Vietnam.Infect Dis Rep. 2024 Sep 29;16(5):932-951. doi: 10.3390/idr16050075. Infect Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 39452160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shimizu A, Hase R, Suzuki D, Toguchi A, Otsuka Y, Hirata N, et al. Lactococcus lactis cholangitis and bacteremia identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: a case report and review of the literature on Lactococcus lactis infection. J Infect Chemother. 2019;25:141–146. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2018.07.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parapouli M, Delbès-Paus C, Kakouri A, Koukkou A-I, Montel M-C, Samelis J. Characterization of a wild, novel nisin A-producing Lactococcus strain with an L. lactis subsp. cremoris genotype and an L. lactis subsp. lactis phenotype, isolated from Greek raw milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:3476–3484. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00436-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

