Comprehensively evaluate the short outcome of small bowel obstruction: A novel medical-economic score system
- PMID: 36998422
- PMCID: PMC10044851
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1509
Comprehensively evaluate the short outcome of small bowel obstruction: A novel medical-economic score system
Abstract
Background: Small bowel obstruction (SBO) still imposes a substantial burden on the health care system. Traditional evaluation systems for SBO outcomes only focus on a single element. The comprehensive evaluation of outcomes for patients with SBO remains poorly studied. Early intensive clinical care would effectively improve the short-term outcomes for SBO, however, the full spectrum of the potential risk status regarding the high complication-cost burden is undetermined.
Aim: We aim to construct a novel system for the evaluation of SBO outcomes and the identification of potential risk status.
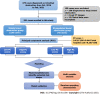
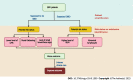
Methods: Patients who were diagnosed with SBO were enrolled and stratified into the simple SBO (SiBO) group and the strangulated SBO (StBO) group. A principal component (PC) analysis was applied for data simplification and the extraction of patient characteristics, followed by separation of the high PC score group and the low PC score group. We identified independent risk status on admission via a binary logistic regression and then constructed predictive models for worsened management outcomes. Receiver operating characteristic curves were drawn, and the areas under the curve (AUCs) were calculated to assess the effectiveness of the predictive models.
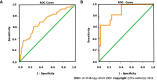
Results: Of the 281 patients, 45 patients (16.0%) were found to have StBO, whereas 236 patients (84.0%) had SiBO. Regarding standardized length of stay (LOS), total hospital cost and the presence of severe adverse events (SAEs), a novel principal component was extracted (PC score = 0.429 × LOS + 0.444 × total hospital cost + 0.291 × SAE). In the multivariate analysis, risk statuses related to poor results for SiBO patients, including a low lymphocyte to monocyte ratio (OR = 0.656), radiological features of a lack of small bowel feces signs (OR = 0.316) and mural thickening (OR = 1.338), were identified as risk factors. For the StBO group, higher BUN levels (OR = 1.478) and lower lymphocytes levels (OR = 0.071) were observed. The AUCs of the predictive models for poor outcomes were 0.715 (95%CI: 0.635-0.795) and 0.874 (95%CI: 0.762-0.986) for SiBO and StBO stratification, respectively.
Conclusion: The novel PC indicator provided a comprehensive scoring system for evaluating SBO outcomes on the foundation of complication-cost burden. According to the relative risk factors, early tailored intervention would improve the short-term outcomes.
Keywords: Intensive clinical care; Outcome evaluation system; Principal component analysis; Radiomics; Risk factors; Small bowel obstruction.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors read and approved the final manuscript and declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bilderback PA, Massman JD 3rd, Smith RK, La Selva D, Helton WS. Small Bowel Obstruction Is a Surgical Disease: Patients with Adhesive Small Bowel Obstruction Requiring Operation Have More Cost-Effective Care When Admitted to a Surgical Service. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;221:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Brandt WS, Wood J, Bhattacharya B, Pei K, Davis KA, Schuster K. Relationship between duration of preoperative symptoms and postoperative ileus for small bowel obstruction. J Surg Res. 2018;225:40–44. - PubMed
-
- Oyasiji T, Angelo S, Kyriakides TC, Helton SW. Small bowel obstruction: outcome and cost implications of admitting service. Am Surg. 2010;76:687–691. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

