Lipid-Laden Macrophage Index as a Diagnostic Tool for Pediatric Aspiration: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36998564
- PMCID: PMC10046735
- DOI: 10.1002/oto2.33
Lipid-Laden Macrophage Index as a Diagnostic Tool for Pediatric Aspiration: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: Lipid-laden macrophage index (LLMI) has been proposed as a marker for aspiration on bronchoalveolar lavage. It has also been studied as a marker for gastroesophageal reflux and other pulmonary diseases. This review aims to determine the clinical correlation between LLMI and pediatric aspiration.
Data sources: PubMed (MeSH search), Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) portals through December 17th, 2020.
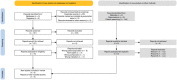
Review methods: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis criteria were followed, and a quality assessment of included studies was performed using the Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies. Search criteria included all occurrences in the title or abstract of the terms "pulmonary aspiration" and "alveolar macrophages."
Results: Five studies describing 720 patients met inclusion, 3 retrospective case-control studies, and 2 prospective observational studies. Four studies suggested a link between elevated LLMI and aspiration, and 1 found no association. Control groups varied and included healthy nonaspirators to nonaspirators with other pulmonary diseases. Diagnosis of aspiration was not standardized across the studies. Three papers proposed cutoff values for LLMI, all different.
Conclusion: The existing literature indicates that LLMI is not a sensitive or specific marker for aspiration. Further study is needed to define the utility of LLMI in pediatric aspiration.
Keywords: aspiration; bronchoalveolar lavage; lipid‐laden macrophages.
© 2023 The Authors. OTO Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Weir KA, McMahon S, Taylor S, Chang AB. Oropharyngeal aspiration and silent aspiration in children. Chest. 2011;140(3):589‐597. - PubMed
-
- Velayutham P, Irace AL, Kawai K, et al. Silent aspiration: who is at risk? Laryngoscope. 2018;128(8):1952‐1957. - PubMed
-
- Torous VF, Brackett D, Brown P, et al. Oil red O staining for lipid‐laden macrophage index of bronchoalveolar lavage: interobserver agreement and challenges to interpretation. J Am Soc Cytopathol. 2020;9(6):563‐569. - PubMed
-
- Kieran SM, Katz E, Rosen R, Khatwa U, Martin T, Rahbar R. The lipid laden macrophage index as a marker of aspiration in patients with type I and II laryngeal clefts. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;74(7):743‐746. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous