Change of metformin concentrations in the liver as a pharmacological target site of metformin after long-term combined treatment with ginseng berry extract
- PMID: 36998615
- PMCID: PMC10043734
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1148155
Change of metformin concentrations in the liver as a pharmacological target site of metformin after long-term combined treatment with ginseng berry extract
Abstract
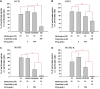
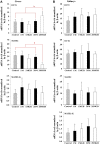
Metformin as an oral glucose-lowering drug is used to treat type 2 diabetic mellitus. Considering the relatively high incidence of cardiovascular complications and other metabolic diseases in diabetic mellitus patients, a combination of metformin plus herbal supplements is a preferrable way to improve the therapeutic outcomes of metformin. Ginseng berry, the fruit of Panax ginseng Meyer, has investigated as a candidate in metformin combination mainly due to its anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, anti-obesity, anti-hepatic steatosis and anti-inflammatory effects. Moreover, the pharmacokinetic interaction of metformin via OCTs and MATEs leads to changes in the efficacy and/or toxicity of metformin. Thus, we assessed how ginseng berry extract (GB) affects metformin pharmacokinetics in mice, specially focusing on the effect of the treatment period (i.e., 1-day and 28-day) of GB on metformin pharmacokinetics. In 1-day and 28-day co-treatment of metformin and GB, GB did not affect renal excretion as a main elimination route of metformin and GB therefore did not change the systemic exposure of metformin. Interestingly, 28-day co-treatment of GB increased metformin concentration in the livers (i.e., 37.3, 59.3% and 60.9% increases versus 1-day metformin, 1-day metformin plus GB and 28-day metformin groups, respectively). This was probably due to the increased metformin uptake via OCT1 and decreased metformin biliary excretion via MATE1 in the livers. These results suggest that co-treatment of GB for 28 days (i.e., long-term combined treatment of GB) enhanced metformin concentration in the liver as a pharmacological target tissue of metformin. However, GB showed a negligible impact on the systemic exposure of metformin in relation to its toxicity (i.e., renal and plasma concentrations of metformin).
Keywords: ginseng berry extract; metformin; multidrug and toxin extrusions; organic cation trans porters; pharmacokinetics; tissue distribution.
Copyright © 2023 Lee, You, Yim, Han, Chae, Bae, Kim, Yu, Jung, Nhoek, Kim, Choi, Chin, Kim and Choi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chae H. S., You B. H., Choi J., Chin Y. W., Kim H., Choi H. S., et al. (2019). Ginseng berry extract enhances metformin efficacy against obesity and hepatic steatosis in mice fed high-fat diet through increase of metformin uptake in liver. J. Funct. Foods 62, 103551. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103551 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

