Anti-tumor effects of low-dose metronomic vinorelbine in combination with alpelisib in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 36998707
- PMCID: PMC10043427
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2022-5064
Anti-tumor effects of low-dose metronomic vinorelbine in combination with alpelisib in breast cancer cells
Abstract
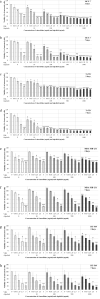
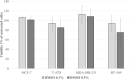
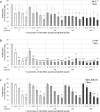
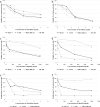
In metastatic breast cancer (MBC), PIK3CA mutations, activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway seem to be associated with chemotherapy resistance and poor outcome. Inhibition of the PI3K signaling pathway may lead to sensitization and prevention of the development of resistance to cytotoxic drugs. The present study aimed to investigate the anti-tumor activity of low-dose vinorelbine (VRL) combined with alpelisib, an α-selective PI3K inhibitor and degrader, in breast cancer (BC) cells. Human BC cell lines MCF-7, T-47D [both hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, PIK3CA-mutated], MDA-MB-231 and BT-549 (both triple-negative, wild-type PIK3CA) were exposed to a combination of low-dose VRL and alpelisib for 3 and 7 days. Cell viability was detected by the Alamar blue assay, and cell proliferation was determined by the BrdU incorporation. The effect of the substances on the p110α protein expression that is encoded by PIK3CA gene was investigated by Western blot. Low-dose VRL plus alpelisib showed synergistic anti-tumor effects and significantly inhibited cell viability and proliferation of MCF-7 and T-47D cells. Even lower alpelisib concentrations (10 ng/ml and 100 ng/ml) combined with low-dose metronomic VRL led to a significant reduction of cell viability of PIK3CA-mutated cells, and the anti-tumor activity was comparable with the effects at 1000 ng/ml alpelisib. Cell viability and proliferation of MDA-MB-231 and BT-549 cells were inhibited by VRL but not by alpelisib alone. This indicates that alpelisib did not significantly affect the cell growth of triple-negative, PIK3CA wild-type BC cells. The p110α expression was downregulated or not affected in PIK3CA-mutated cell lines, and not significantly upregulated in PIK3CA wild-type cell lines. In conclusion, combination of low-dose metronomic VRL and alpelisib showed synergistic anti-tumor effects and significantly inhibited the growth of HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated BC cells, providing a rationale for further efforts to evaluate this combination in vivo.
Keywords: PIK3CA mutation; alpelisib; breast cancer; low-dose metronomic chemotherapy; vinorelbine.
Copyright © 2023 Krajnak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SK received speaker honoraria from Roche Pharma AG and Novartis Pharma GmbH Germany, research funding from Novartis Pharma GmbH Germany and travel reimbursement from PharmaMar and Novartis Pharma GmbH Germany. KA received speaker honoraria from Clovis Oncology, MSD und AstraZeneca. ASH received speaker honoraria from Pfizer Pharma GmbH and honoraria from Medupdate GmbH. MS received honoraria for speaker or consultancy role from AMGEN, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Lilly, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, and Roche. He received research funding from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Eisai, Genentech, Myelo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pantarhei Bioscience, Pfizer, Pierre-Fabre, and Roche Pharma AG. He received travel reimbursement from Pfizer and Roche. In addition, MS has a patent for EP 2390370 B1 issued and a patent for EP 2951317 B1issued. MJB received honoraria and expenses from Astra Zeneca, Clovis Oncology, GSK, MSD, Pharma Mar, Roche Pharma AG and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. He is consultant to Eisai, GSK, MSD, Pharma Mar, Roche Pharma AG and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. He received funded research from AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, MSD and Novartis. AH received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Celegen, MedConcept Gm, Med update GmbH, Medicultus, Pfizer, Promedicis GmbH, Pierre Fabre, Softconsult, Roche Pharma AG, Streamedup!GmbH and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. She is a member of the advisory board of PharmaMar, Promedicis GmbH, Pierre Fabre Pharma GmbH, Roche Pharma AG and Tesaro Bio Germany GmbH. She received research funding from Celgene. All remaining authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic actions of Alpelisib and Melatonin in breast cancer cell lines with PIK3CA gene mutation.Life Sci. 2023 Jul 1;324:121708. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121708. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37086897
-
The effect of the alpha-specific PI3K inhibitor alpelisib combined with anti-HER2 therapy in HER2+/PIK3CA mutant breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 4;13:1108242. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1108242. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37469415 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus versus alpelisib in advanced hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative breast cancer: targeting different nodes of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway with different clinical implications.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 6;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01271-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32252811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: final overall survival results from SOLAR-1.Ann Oncol. 2021 Feb;32(2):208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.011. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Ann Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33246021 Clinical Trial.
-
A pharmacokinetic evaluation of alpelisib for the treatment of HR+, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021 Feb;17(2):139-152. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2021.1844662. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33213227 Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming Breast Cancer Drug Resistance: A Novel Approach Using siRNA-Mediated P-glycoprotein Downregulation to Enhance Vinorelbine Efficacy.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Jul;14(2):445-452. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.030. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39206391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aapro M, Ruiz-Borrego M, Hegg R, Kukielka-Budny B, Morales S, Cinieri S, et al. Randomized phase II study evaluating weekly oral vinorelbine versus weekly paclitaxel in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative patients with advanced breast cancer (NorBreast-231 trial) Breast. 2019;45:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Andre F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1929–1940. - PubMed
-
- Andre F, Ciruelos EM, Juric D, Loibl S, Campone M, Mayer IA, et al. Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: final overall survival results from SOLAR-1. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:208–217. - PubMed
-
- Andre N, Tsai K, Carre M, Pasquier E. Metronomic chemotherapy: direct targeting of cancer cells after all? Trends Cancer. 2017;3:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Badinloo M, Esmaeili-Mahani S. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases inhibitor LY294002 potentiates the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin, vincristine, and etoposide in a panel of cancer cell lines. Fund Clin Pharmacol. 2014;28:414–422. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
