Coalitionality shapes moral elevation: evidence from the U.S. Black Lives Matter protest and counter-protest movements
- PMID: 36998761
- PMCID: PMC10049748
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.220990
Coalitionality shapes moral elevation: evidence from the U.S. Black Lives Matter protest and counter-protest movements
Abstract
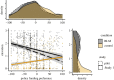
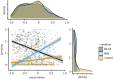
Witnessing altruistic behaviour can elicit moral elevation, an emotion that motivates prosocial cooperation. This emotion is evoked more strongly when the observer anticipates that other people will be reciprocally cooperative. Coalitionality should therefore moderate feelings of elevation, as whether the observer shares the coalitional affiliation of those observed should influence the observer's assessment of the likelihood that the latter will cooperate with the observer. We examined this thesis in studies contemporaneous with the 2020 Black Lives Matter (BLM) protests. Although BLM protests were predominantly peaceful, they were depicted by conservative media as destructive and antisocial. In two large-scale, pre-registered online studies (total N = 2172), political orientation strongly moderated feelings of state elevation elicited by a video of a peaceful BLM protest (Studies 1 and 2) or a peaceful Back the Blue (BtB) counter-protest (Study 2). Political conservatism predicted less elevation following the BLM video and more elevation following the BtB video. Elevation elicited by the BLM video correlated with preferences to defund police, whereas elevation elicited by the BtB video correlated with preferences to increase police funding. These findings extend prior work on elevation into the area of prosocial cooperation in the context of coalitional conflict.
Keywords: coalitional psychology; elevation; emotion; political orientation; prosociality.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Newkirk VR. 2016. The permanence of Black Lives Matter. The Atlantic. See https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2016/08/movement-black-live....
-
- Oatley K, Johnson-Laird PN. 1987. Towards a cognitive theory of emotions. Cogn. Emotion l, 29-50. ( 10.1080/02699938708408362) - DOI
-
- Tooby J, Cosmides L. 2008. The evolutionary psychology of the emotions and their relationship to internal regulatory variables. In Handbook of emotions (eds Lewis M, Haviland-Jones JM, Barrett LF), pp. 114-137. New York, NY: Guilford; Press.
-
- Tooby J, Cosmides L, Sell A, Lieberman D, Sznycer D. 2008. Internal regulatory variables and the design of human motivation: a computational and evolutionary approach. In Handbook of approach and avoidance motivation (eds Elliot AJ), pp. 251-271. Mahwah, NJ: Psychology Press.
