Decoding the crosstalk between mevalonate metabolism and T cell function
- PMID: 36999733
- PMCID: PMC12136499
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.13200
Decoding the crosstalk between mevalonate metabolism and T cell function
Abstract
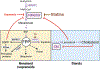
The mevalonate pathway is an essential metabolic pathway in T cells regulating development, proliferation, survival, differentiation, and effector functions. The mevalonate pathway is a complex, branched pathway composed of many enzymes that ultimately generate cholesterol and nonsterol isoprenoids. T cells must tightly control metabolic flux through the branches of the mevalonate pathway to ensure sufficient isoprenoids and cholesterol are available to meet cellular demands. Unbalanced metabolite flux through the sterol or the nonsterol isoprenoid branch is metabolically inefficient and can have deleterious consequences for T cell fate and function. Accordingly, there is tight regulatory control over metabolic flux through the branches of this essential lipid synthetic pathway. In this review we provide an overview of how the branches of the mevalonate pathway are regulated in T cells and discuss our current understanding of the relationship between mevalonate metabolism, cholesterol homeostasis and T cell function.
Keywords: T cells; cholesterol; isoprenoids; mevalonate pathway; statins.
© 2023 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics Declaration
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the contents of this article.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

