Exosomal miR-370-3p increases the permeability of blood-brain barrier in ischemia/reperfusion stroke of brain by targeting MPK1
- PMID: 37000151
- PMCID: PMC10085611
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204573
Exosomal miR-370-3p increases the permeability of blood-brain barrier in ischemia/reperfusion stroke of brain by targeting MPK1
Abstract
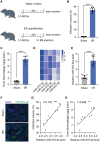
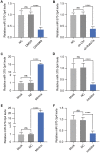
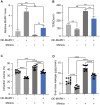
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) damage induced by stroke poses a serious hazard to human life, while mechanism of blood-brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction is still unknown. To imitate stroke induced ischemia conditions in vivo, the rat model of cerebral I/R damage was created by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). In vitro, the rat microvascular endothelial cell line bEND.3 was subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R). Evans blue was used to evaluate the permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To evaluate gene expression at the mRNA and protein levels, researchers used real-time PCR and western blotting. Infarct volume and BBB permeability were considerably higher in cerebral (I/R) animals than in the Sham group. Exosomal miR-370-3p expression was shown to be higher in the brains of I/R injured rats and OGD/R treatment bEND.3. The BBB permeability was considerably increased when miR-370-3p was downregulated in OGD/R pretreated bEND.3. miR-370-3p regulates MAPK1 expression by targeting it. In bEND.3, OGD/R therapy increased BBB permeability substantially. OGD/R was inhibited by miR-370-3p mimic transfection, while miR-370-3p mimic was abolished by co-transfection with MAPK1 overexpression lentivirus. In cerebral I/R damage, exosomal miR-370-3p targets MAPK1 and aggregates BBB permeability.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; exosomes; ischemia/reperfusion; mir-370-3p; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
MiR-539 Targets MMP-9 to Regulate the Permeability of Blood-Brain Barrier in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury of Brain.Neurochem Res. 2018 Dec;43(12):2260-2267. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2646-0. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30276507
-
miR-671-5p Upregulation Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in the Ischemia Stroke Model Via the NF-кB/MMP-9 Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;60(7):3824-3838. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03318-7. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36949221
-
Inhibition of miR-19a-3p decreases cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting IGFBP3 in vivo and in vitro.Biol Res. 2020 Apr 20;53(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00280-9. Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32312329 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxidative stress in blood-brain barrier disruption during ischemic stroke: Antioxidants in clinical trials.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;228:116186. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116186. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38561092 Review.
-
Nanoparticles Designed Based on the Blood-Brain Barrier for the Treatment of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Small. 2025 May;21(19):e2410404. doi: 10.1002/smll.202410404. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Small. 2025. PMID: 40042407 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum exosomal miRNA contributes to the diagnosis of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis.J Neurooncol. 2025 Jun;173(2):419-428. doi: 10.1007/s11060-025-04999-x. Epub 2025 Mar 13. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 40080246 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle Profiling Reveals Novel Autism Signatures in Patient-Derived Forebrain Organoids.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 May 13:rs.3.rs-6573757. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6573757/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40470213 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Exosomes: A Cellular Communication Medium That Has Multiple Effects On Brain Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6864-6892. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03957-4. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38356095 Review.
-
Roles and Potential Mechanisms of Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Oct;16(5):1836-1849. doi: 10.1007/s12975-025-01334-4. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39918683 Review.
-
Exploring the therapeutic efficacy and pharmacological mechanism of Guizhi Fuling Pill on ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis and network pharmacology analysis.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Aug;39(6):1157-1174. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01383-y. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39052207
References
-
- Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Adams RJ, Berry JD, Brown TM, Carnethon MR, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, et al., and American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2011 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011; 123:e18–209. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182009701 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto M, Suenaga J, Takase H, Araki K, Yao T, Fujimura T, Murayama K, Okumura K, Ueno R, Shimizu N, Kawahara N, Yamamoto T, Seko Y. Oxidative stress-responsive apoptosis inducing protein (ORAIP) plays a critical role in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:13512. 10.1038/s41598-019-50073-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

