The Insulin-Only Bionic Pancreas Improves Glycemic Control in Non-Hispanic White and Minority Adults and Children With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 37000680
- PMCID: PMC10234742
- DOI: 10.2337/dc22-1478
The Insulin-Only Bionic Pancreas Improves Glycemic Control in Non-Hispanic White and Minority Adults and Children With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the performance of the iLet bionic pancreas (BP) in non-Hispanic White individuals (here referred to as "Whites") and in Black, Hispanic, and other individuals (here collectively referred to as "Minorities").
Research design and methods: A multicenter, randomized controlled trial evaluated glycemic management with the BP versus standard of care (SC) in 161 adult and 165 pediatric participants with type 1 diabetes over 13 weeks.
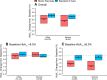
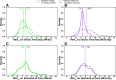
Results: In Whites (n = 240), the mean baseline-adjusted difference in 13-week HbA1c between the BP and SC groups was -0.45% (95% CI -0.61 to -0.29 [-4.9 mmol/mol; -6.6 to -3.1]; P < 0.001), while this difference among Minorities (n = 84) was -0.53% (-0.83 to -0.24 [-6.0 mmol/mol; -9.2 to -2.8]; P < 0.001). In Whites, the mean baseline-adjusted difference in time in range between the BP and SC groups was 10% (95% CI 7-12; P < 0.001) and in Minorities was 14% (10-18; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The BP improves glycemic control in both Whites and Minorities and offers promise in decreasing health care disparities.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lado JJ, Lipman TH. Racial and ethnic disparities in the incidence, treatment, and outcomes of youth with type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2016;45:453–461 - PubMed

