Implementation and Uptake of Raltegravir Granules in Newborns Diagnosed With HIV Through Birth Testing in Maternity Settings in Zimbabwe During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37000925
- PMCID: PMC10289070
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0000000000003906
Implementation and Uptake of Raltegravir Granules in Newborns Diagnosed With HIV Through Birth Testing in Maternity Settings in Zimbabwe During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
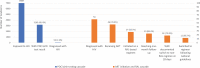
Zimbabwe introduced raltegravir (RAL) granules at 14 facilities providing point-of-care HIV birth testing, aiming to initiate all newborns with HIV on a RAL-based regimen. From June 2020 to July 2021, we tested 3172 of the 6989 (45%) newborns exposed to HIV; we diagnosed 59(2%) with HIV infection, of whom 27 (46%) initiated RAL. The SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus disease pandemic exacerbated supply chain and trained provider shortages, contributing to low birth testing, RAL uptake and 6-month viral load testing.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS epidemiological estimates. 2021. Available at: https://aidsinfo.unaids.org/. Accessed June 7, 2022.
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Therapy and Medical Management of Children Living with HIV. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in pediatric HIV infection. Available at: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/Pe.... Accessed June 7, 2022.
-
- World Health Organization. HIV drug resistance report. 2019. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-CDS-HIV-19.21. Accessed June 7, 2022.
-
- Zimbabwe Ministry of Health and Child Care. National HIV treatment guidelines. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous