Baseline PET radiomics outperforms the IPI risk score for prediction of outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 37001036
- PMCID: PMC10646814
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018558
Baseline PET radiomics outperforms the IPI risk score for prediction of outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
The objective of this study is to externally validate the clinical positron emission tomography (PET) model developed in the HOVON-84 trial and to compare the model performance of our clinical PET model using the international prognostic index (IPI). In total, 1195 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) were included in the study. Data of 887 patients from 6 studies were used as external validation data sets. The primary outcomes were 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) and 2-year time to progression (TTP). The metabolic tumor volume (MTV), maximum distance between the largest lesion and another lesion (Dmaxbulk), and peak standardized uptake value (SUVpeak) were extracted. The predictive values of the IPI and clinical PET model (MTV, Dmaxbulk, SUVpeak, performance status, and age) were tested. Model performance was assessed using the area under the curve (AUC), and diagnostic performance, using the positive predictive value (PPV). The IPI yielded an AUC of 0.62. The clinical PET model yielded a significantly higher AUC of 0.71 (P < .001). Patients with high-risk IPI had a 2-year PFS of 61.4% vs 51.9% for those with high-risk clinical PET, with an increase in PPV from 35.5% to 49.1%, respectively. A total of 66.4% of patients with high-risk IPI were free from progression or relapse vs 55.5% of patients with high-risk clinical PET scores, with an increased PPV from 33.7% to 44.6%, respectively. The clinical PET model remained predictive of outcome in 6 independent first-line DLBCL studies, and had higher model performance than the currently used IPI in all studies.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.F.B. received departmental funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer and Takeda. M.E.D.C. received financial support for the clinical trials from Celgene, BMS and Gilead. J.M.Z. received financial support for clinical trials from Roche, Gilead, and Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
A complete list of the members of the PETRA Consortium appears in the supplemental Appendix.
Figures
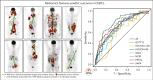


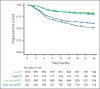

Comment in
-
A man's best friend is his PET.Blood. 2023 Jun 22;141(25):3010-3012. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023020325. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37347501 No abstract available.
References
-
- International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):987–994. - PubMed
-
- Habermann TM, Weller EA, Morrison VA, et al. Rituximab-CHOP versus CHOP alone or with maintenance rituximab in older patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(19):3121–3127. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson M, Counsell N, Cunningham D, et al. Prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: an analysis of the UK National Cancer Research Institute R-CHOP 14 versus 21 phase 3 trial. Br J Haematol. 2021;192(6):1015–1019. - PubMed
-
- Ruppert AS, Dixon JG, Salles G, et al. International prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a comparison of IPI, R-IPI, and NCCN-IPI. Blood. 2020;135(23):2041–2048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

