Age-dependent Pdgfrβ signaling drives adipocyte progenitor dysfunction to alter the beige adipogenic niche in male mice
- PMID: 37002214
- PMCID: PMC10066302
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37386-z
Age-dependent Pdgfrβ signaling drives adipocyte progenitor dysfunction to alter the beige adipogenic niche in male mice
Abstract
Perivascular adipocyte progenitor cells (APCs) can generate cold temperature-induced thermogenic beige adipocytes within white adipose tissue (WAT), an effect that could counteract excess fat mass and metabolic pathologies. Yet, the ability to generate beige adipocytes declines with age, creating a key challenge for their therapeutic potential. Here we show that ageing beige APCs overexpress platelet derived growth factor receptor beta (Pdgfrβ) to prevent beige adipogenesis. We show that genetically deleting Pdgfrβ, in adult male mice, restores beige adipocyte generation whereas activating Pdgfrβ in juvenile mice blocks beige fat formation. Mechanistically, we find that Stat1 phosphorylation mediates Pdgfrβ beige APC signaling to suppress IL-33 induction, which dampens immunological genes such as IL-13 and IL-5. Moreover, pharmacologically targeting Pdgfrβ signaling restores beige adipocyte development by rejuvenating the immunological niche. Thus, targeting Pdgfrβ signaling could be a strategy to restore WAT immune cell function to stimulate beige fat in adult mammals.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
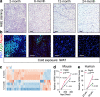
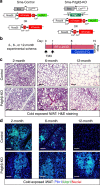

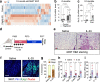
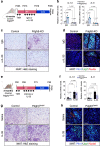

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

