Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37002802
- PMCID: PMC10235887
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13221
Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Sarcopenia is an age-related disease and is often accompanied by other diseases. Now, many studies have shown that cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) may raise the incidence rate of sarcopenia. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the prevalence of sarcopenia in patients with CVDs compared with the general population, defined as relatively healthy non-hospitalized subjects. The databases of PubMed, Embase, Medline and Web of Science were searched for eligible studies published up to 12 November 2022. Two assessment tools were used to evaluate study quality and the risk of bias. Statistical analysis was conducted using STATA 14.0 and R Version 4.1.2. Thirty-eight out of the 89 629 articles retrieved were included in our review. The prevalence of sarcopenia ranged from 10.1% to 68.9% in patients with CVDs, and the pooled prevalence was 35% (95% confidence interval [95% CI]: 28-42%). The pooled prevalence of sarcopenia was 32% (95% CI: 23-41%) in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF), 61% (95% CI: 49-72%) in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF), 43% (95% CI: 2-85%) in patients with coronary artery disease, 30% (95% CI: 25-35%) in patients with cardiac arrhythmia (CA), 35% (95% CI: 10-59%) in patients with congenital heart disease and 12% (95% CI: 7-17%) in patients with unclassed CVDs. However, in the general population, the prevalence of sarcopenia varied from 2.9% to 28.6% and the pooled prevalence was 13% (95% CI: 9-17%), suggesting that the prevalence of sarcopenia in patients with CVDs was about twice compared with the general population. The prevalence of sarcopenia was significantly higher only in patients with ADHF, CHF and CA compared with the general population. There is a positive correlation between CVDs and sarcopenia. The prevalence of sarcopenia is higher in patients with CVDs than that in the general population. With global aging, sarcopenia has brought a heavy burden to individuals and society. Therefore, it is important to identify the populations with high-risk or probable sarcopenia in order to do an early intervention, such as exercise, to counteract or slow down the progress of sarcopenia.
Keywords: cardiac arrhythmia; cardiovascular diseases; coronary artery disease; heart failure; prevalence; sarcopenia.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
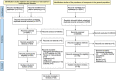
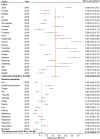

Comment in
-
Comment on "Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis" by Zuo et al.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023 Dec;14(6):2988-2990. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13382. Epub 2023 Nov 8. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023. PMID: 37941311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenberg IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr 1997;127:990S–991S. - PubMed
-
- Cruz‐Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. The Lancet 2019;393:2636–2646. - PubMed
-
- Cao L, Morley JE. Sarcopenia is recognized as an independent condition by an International Classification of Disease, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD‐10‐CM) code. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2016;17:675–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

