Modalities to Deliver Cell Therapy for Treatment of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- PMID: 37002893
- PMCID: PMC11305013
- DOI: 10.1089/wound.2022.0114
Modalities to Deliver Cell Therapy for Treatment of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
Abstract
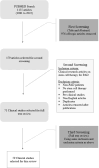
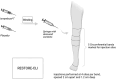
Significance: Chronic limb threatening ischemia (CLTI) is a severe form of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) that is associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality, and especially limb loss. In patients with no options for revascularization, stem cell therapy is a promising treatment option. Recent Advances: Cell therapy directly delivered to the affected ischemic limb has been shown to be a safe, effective, and feasible therapeutic alternative for patients with severe PAD. Multiple methods for cell delivery, including local, regional, and combination approaches, have been examined in both pre-clinical studies and clinical trials. This review focuses on delivery modalities used in clinical trials that deliver cell therapy to patients with severe PAD. Critical Issues: Patients with CLTI are at high risk for complications of the disease, such as amputations, leading to a poor quality of life. Many of these patients do not have viable options for revascularization using traditional interventional or surgical methods. Clinical trials have shown therapeutic benefit for cell therapy in these patients, but methods of cell treatment are not standardized, including the method of cell delivery to the ischemic limb. Future Directions: The ideal delivery approach for stem cell therapy in PAD patients remains unclear. Further studies are needed to determine the best modality of cell delivery to maximize clinical benefits.
Keywords: PAD; peripheral artery disease; peripheral vascular disease; stem cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy (REGENACIP®), a promising treatment option in chronic limb threatening ischemia - a narrative review.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Oct 8;15(1):352. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03957-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39380065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global vascular guidelines on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia.J Vasc Surg. 2019 Jun;69(6S):3S-125S.e40. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 May 28. J Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 31159978 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of autologous adipose-derived stem cell therapy for ulcers in patients with critical limb ischemia.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 9;20(4):e0318922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318922. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40202953 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Autologous Cell Therapy in Diabetic Patients with Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10184. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810184. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Appropriate care in chronic limb threatening ischemia: A review of current evidence and outcomes.Semin Vasc Surg. 2024 Jun;37(2):249-257. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2024.04.001. Epub 2024 Apr 7. Semin Vasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 39152003 Review.
References
-
- Fowkes FG, Rudan D, Rudan I, et al. . Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013;382(9901):1329–1340. - PubMed
-
- Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, et al. . Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). J Vasc Surg 2007;45(Suppl S):S5–S67. - PubMed
-
- Sachs T, Pomposelli F, Hamdan A, et al. . Trends in the national outcomes and costs for claudication and limb threatening ischemia: Angioplasty vs bypass graft. J Vasc Surg 2011;54(4):1021..e1–1031.e1. - PubMed
-
- Farber A, Menard MT, Conte MS, et al. . Surgery or endovascular therapy for chronic limb-threatening ischemia. N Engl J Med 2022;387(25):2305–2316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

