Black queen cell virus detected in Canadian mosquitoes
- PMID: 37004145
- PMCID: PMC10066845
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/iead016
Black queen cell virus detected in Canadian mosquitoes
Abstract
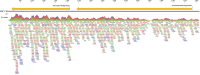
Black queen cell virus (BQCV) is a ubiquitous honeybee virus and a significant pathogen to queen bee (Apis mellifera) larvae. However, many aspects of the virus remain poorly understood, including the transmission dynamics. In this study, we used next-generation sequencing to identify BQCV in Aedes vexans (n = 4,000) collected in 2019 and 2020 from Manitoba, Canada. We assembled de novo the nearly complete (>96%) genome sequence of the virus, which is the first available from North America and the first report of BQCV being harbored by mosquitoes. Phylogenetic tree reconstructions indicated that the genome had 95.5% sequence similarity to a BQCV isolate from Sweden. Sequences of a potential vector (Varroa destructor) and a microsporidian associated with BQCV (Nosema apis) were not identified in the mosquito samples, however, we did detect sequences of plant origin. We, therefore, hypothesize that the virus was indirectly acquired by mosquitoes foraging at the same nectar sources as honeybees.
Keywords: Aedes; Picornavirales; apiary; nectar; transmission.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Entomological Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Allen M, Ball B.. The incidence and world distribution of the honey bee viruses. Bee World. 1996:77(3):141–162. 10.1080/0005772x.1996.11099306 - DOI
-
- Chadee DD, Sutherland JM, Gilles JRL.. Diel sugar feeding and reproductive behaviours of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in Trinidad: with implications for mass release of sterile mosquitoes. Acta Trop. 2014:132:S86–S90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

