Haemato-biochemical, mutagenic, and histopathological changes in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to BTX
- PMID: 37004609
- PMCID: PMC10163093
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-023-26604-2
Haemato-biochemical, mutagenic, and histopathological changes in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to BTX
Abstract
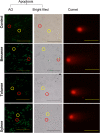
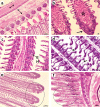
The study of the DNA damage response in erythrocytes after exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can present evidence for its potential effect as genotoxic- biomarkers for environmental pollution. Although VOCs are dangerous pollutants, still little is known about hemotoxic, cytotoxic, and genotoxic effects of such pollutants on fish. We optimized an assay method for apoptosis and DNA damage in erythrocytes of adult tilapia fish after 15 days exposure to benzene (0.762 ng/L), toluene (26.614 ng/L), and xylene (89.403 ng/L). The highest level of apoptosis and DNA damage were recorded in benzene-exposed fish, as was the highest level of histopathological alterations in gills, liver, and kidney. The imbalance of the antioxidants profile explained the stress-case reported in exposed fish. These results suggest that hemotoxic, cytotoxic, genotoxic, and tissue damage were recorded after exposure to BTX in Oreochromis niloticus.
Keywords: Acridine orange; BTX; DNA damage; Erythrocytes; Fish.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abou Khalil NS, Abd-Elkareem M, Sayed AH. Nigella sativa seed protects against 4-nonylphenol-induced haematotoxicity in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822): oxidant/antioxidant rebalance. Aquat Nutr. 2017;23:1467–1474.
-
- Adewoye SO. A comparative study on the behavioral responses of Clarias gariepinus on exposure to soap and detergent effluent. Adv Appl Res. 2010;1:89–95.
-
- Aebi H (1984): [13] Catalase in vitro, Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, pp. 121–126 - PubMed
-
- AFS-FHS (2017): FHS Blue Book: Suggested procedures for the detection and identification of certain finfish and shellfish pathogens
-
- Ahmad S, Singh V, Rao GS. Antioxidant potential in serum and liver of albino rats exposed to benzene. Indian J Exp Biol. 1994;32:203–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

