Clinical Impacts of Stereotactic Electroencephalography on Epilepsy Surgery and Associated Issues in the Current Situation in Japan
- PMID: 37005247
- PMCID: PMC10241538
- DOI: 10.2176/jns-nmc.2022-0271
Clinical Impacts of Stereotactic Electroencephalography on Epilepsy Surgery and Associated Issues in the Current Situation in Japan
Abstract
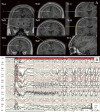
Stereotactic electroencephalography (SEEG) is receiving increasing attention as a safe and effective technique in the invasive evaluation for epileptogenic zone (EZ) detection. The main clinical question is whether the use of SEEG truly improves outcomes. Herein, we compared outcomes in our patients after three types of intracranial EEG (iEEG): SEEG, the subdural electrode (SDE), and a combined method using depth and strip electrodes. We present here our preliminary results from two demonstrative cases. Several international reports from large epilepsy centers found the following clinical advantages of SEEG: 1) three-dimensional analysis of structures, including bilateral and multilobar structures; 2) low rate of complications; 3) less pneumoencephalopathy and less patient burden during postoperative course, which allows the initiation of video-EEG monitoring immediately after implantation and does not require resection to be performed in the same hospitalization; and 4) a higher rate of good seizure control after resection. In other words, SEEG more accurately identified the EZ than the SDE method. We obtained similar results in our preliminary experiences under limited conditions. In Japan, as of August 2022, dedicated electrodes and SEEG accessories have not been approved and the use of the robot arm is not widespread. The Japanese medical community is hopeful that these issues will soon be resolved and that the experience with SEEG in Japan will align with that of large epilepsy centers internationally.
Keywords: complication; epilepsy surgery; focal epilepsy; outcomes; stereotactic electroencephalography (SEEG).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest (COIs) regarding this article according to the criteria of The Japan Neurosurgical Society. They have completed the self-reported registration of their COI status to the society.
Figures


References
-
- Bancaud J, Angelergues R, Bernouilli C, et al. : Functional stereotaxic exploration (SEEG) of epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 28: 85-86, 1970 - PubMed
-
- Cardinale F, Cossu M, Castana L, et al. : Stereoelectroencephalography: Surgical methodology, safety, and stereotactic application accuracy in 500 procedures. Neurosurgery 72: 353-366, 2013 - PubMed
-
- González-Martínez J, Bulacio J, Thompson S, et al. : Technique, results, and complications related to robot-assisted stereoelectroencephalography. Neurosurgery 78: 169-180, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Talairach J, Bancaud J: Stereotaxic approach to epilepsy methodology of anatomo-functional stereotaxic investigations. Prog Neurol Surg Basel 297-354, 1973
-
- Bancaud J: Surgery of epilepsy based on stereotactic investigations–the plan of the SEEG investigation. Acta Neurochir Suppl 30: 25-34, 1980 - PubMed

