Immunoglobulin G4-related Hepatopathy after COVID-19 Vaccination
- PMID: 37005259
- PMCID: PMC10400404
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1634-23
Immunoglobulin G4-related Hepatopathy after COVID-19 Vaccination
Abstract
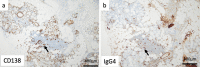
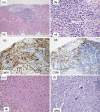
An 84-year-old woman with IgG4-related disease presented with jaundice and liver dysfunction after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination. Serum IgG4 levels were elevated. Diagnostic imaging showed no stenotic lesions in the bile ducts. A liver biopsy was performed because of the enlarged liver. Infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells, which accounted for approximately 74% of total plasma cells, was found in the portal area, but there was no evidence of periportal hepatitis, and inflammatory cell infiltration into the lobular space was minimal. IgG4-related hepatopathy was diagnosed. The patient achieved spontaneous remission with no treatment and only follow-up and remains under observation at the time of writing.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccination; IgG4-related hepatopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Perugino CA, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16: 702-714, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Umemura T, Zen Y, Hamano H, et al. Immunoglobin G4-hepatopathy: association of immunoglobin G4-bearing plasma cells in liver with autoimmune pancreatitis. Hepatology 46: 463-471, 2007. - PubMed

