LinChemIn: SynGraph-a data model and a toolkit to analyze and compare synthetic routes
- PMID: 37005691
- PMCID: PMC10067316
- DOI: 10.1186/s13321-023-00714-y
LinChemIn: SynGraph-a data model and a toolkit to analyze and compare synthetic routes
Abstract
Background: The increasing amount of chemical reaction data makes traditional ways to navigate its corpus less effective, while the demand for novel approaches and instruments is rising. Recent data science and machine learning techniques support the development of new ways to extract value from the available reaction data. On the one side, Computer-Aided Synthesis Planning tools can predict synthetic routes in a model-driven approach; on the other side, experimental routes can be extracted from the Network of Organic Chemistry, in which reaction data are linked in a network. In this context, the need to combine, compare and analyze synthetic routes generated by different sources arises naturally.
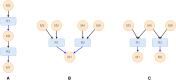
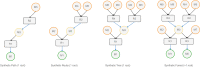
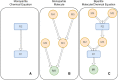
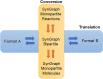
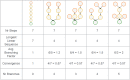
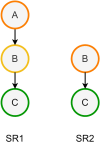
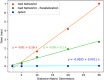
Results: Here we present LinChemIn, a python toolkit that allows chemoinformatics operations on synthetic routes and reaction networks. Wrapping some third-party packages for handling graph arithmetic and chemoinformatics and implementing new data models and functionalities, LinChemIn allows the interconversion between data formats and data models and enables route-level analysis and operations, including route comparison and descriptors calculation. Object-Oriented Design principles inspire the software architecture, and the modules are structured to maximize code reusability and support code testing and refactoring. The code structure should facilitate external contributions, thus encouraging open and collaborative software development.
Conclusions: The current version of LinChemIn allows users to combine synthetic routes generated from various tools and analyze them, and constitutes an open and extensible framework capable of incorporating contributions from the community and fostering scientific discussion. Our roadmap envisages the development of sophisticated metrics for routes evaluation, a multi-parameter scoring system, and the implementation of an entire "ecosystem" of functionalities operating on synthetic routes. LinChemIn is freely available at https://github.com/syngenta/linchemin.
Keywords: Chemoinformatics; Computer-aided synthesis planning; Reaction.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Schwaller P, Vaucher AC, Laplaza R, Bunne C, Krause A, Corminboeuf C, Laino T. Machine intelligence for chemical reaction space. WIREs Comput Mol Sci. 2022 doi: 10.1002/wcms.1604. - DOI
-
- Jiang Y, Yu Y, Kong M, Mei Y, Yuan L, Huang Z, Kuang K, Wang Z, Yao H, Zou J, Coley CW, Wei Y. Artificial intelligence for retrosynthesis prediction. Engineering. 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.04.021. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

