Multiplatform untargeted metabolomics
- PMID: 37005774
- PMCID: PMC10948111
- DOI: 10.1002/mrc.5350
Multiplatform untargeted metabolomics
Abstract
Metabolomics samples like human urine or serum contain upwards of a few thousand metabolites, but individual analytical techniques can only characterize a few hundred metabolites at best. The uncertainty in metabolite identification commonly encountered in untargeted metabolomics adds to this low coverage problem. A multiplatform (multiple analytical techniques) approach can improve upon the number of metabolites reliably detected and correctly assigned. This can be further improved by applying synergistic sample preparation along with the use of combinatorial or sequential non-destructive and destructive techniques. Similarly, peak detection and metabolite identification strategies that employ multiple probabilistic approaches have led to better annotation decisions. Applying these techniques also addresses the issues of reproducibility found in single platform methods. Nevertheless, the analysis of large data sets from disparate analytical techniques presents unique challenges. While the general data processing workflow is similar across multiple platforms, many software packages are only fully capable of processing data types from a single analytical instrument. Traditional statistical methods such as principal component analysis were not designed to handle multiple, distinct data sets. Instead, multivariate analysis requires multiblock or other model types for understanding the contribution from multiple instruments. This review summarizes the advantages, limitations, and recent achievements of a multiplatform approach to untargeted metabolomics.
Keywords: mass spectrometry; metabolite assignment; metabolome coverage; metabolomics; multiplatform; nuclear magnetic resonance.
© 2023 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

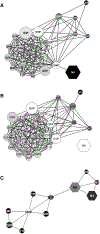
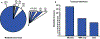
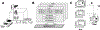
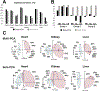
References
-
- Di Minno A, Gelzo M, Stornaiuolo M, Ruoppolo M, Castaldo G, Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2021, 31, 1645–1652. - PubMed
-
- Katam R, Lin C, Grant K, Katam CS, Chen S, International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 6985; - PMC - PubMed
- Jin L, Godri Pollitt KJ, Liew Z, Rosen Vollmar AK, Vasiliou V, Johnson CH, Zhang Y, Current Environmental Health Reports 2021, 8, 7–22; - PubMed
- Wei S, Wei Y, Gong Y, Chen Y, Cui J, Li L, Yan H, Yu Y, Lin X, Li G, Yi L, Metabolomics 2022, 18, 35. - PubMed
-
- Lacalle-Bergeron L, Izquierdo-Sandoval D, Sancho JV, López FJ, Hernández F, Portolés T, TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2021, 135, 116161;
- Jacobs DM, van den Berg MA, Hall RD, Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2021, 70, 23–28. - PubMed
-
- Duarte NC, Becker SA, Jamshidi N, Thiele I, Mo ML, Vo TD, Srivas R, Palsson BØ, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 1777–1782; - PMC - PubMed
- Graham E, Lee J, Price M, Tarailo-Graovac M, Matthews A, Engelke U, Tang J, Kluijtmans LAJ, Wevers RA, Wasserman WW, van Karnebeek CDM, Mostafavi S, Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 2018, 41, 435–445. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

