Visual Acuity Outcomes in Patients Receiving Frequent Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration in Clinical Practice
- PMID: 37006507
- PMCID: PMC9979036
- DOI: 10.1177/2474126420960896
Visual Acuity Outcomes in Patients Receiving Frequent Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration in Clinical Practice
Abstract
Purpose: This work evaluates dosing frequency with intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents over 2 years and visual acuity (VA) outcomes in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD).
Methods: This retrospective analysis assesses electronic medical record data (Vestrum Health treatment and outcomes database) of newly diagnosed nAMD in patients who were initiated on intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment at US clinical sites. Eyes were divided into 2 injection frequency subcohorts (≤ 6 or > 6 injections/y); treatment frequency and change in mean VA (Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study letters) were evaluated.
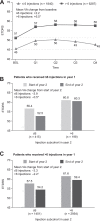
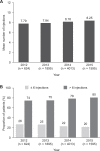
Results: Overall, 8127 of 213 824 eyes met inclusion criteria in year 1 and 4968 in year 2. During year 1, 77% of the eyes received more than 6 injections (n = 6287), the majority of which received injections at the same frequency during year 2. Mean VA gain from baseline at year 1 was lower in the ≤ 6 than > 6 injections/y subcohort (2.2 vs 6.5, P < .001). Decrease in mean VA from the end of year 1 to year 2 was significantly greater for eyes administered 6 or fewer injections in year 2 than those that received more frequent injections, irrespective of the frequency of injections in the first year.
Conclusions: In routine clinical practice, most eyes with nAMD that completed at least 1 year of follow-up were treated with more than 6 injections of anti-VEGF agents during the first year of treatment, resulting in better VA gains than eyes treated less frequently during the same period.
Keywords: antivascular endothelial growth factor; bevacizumab; intravitreal aflibercept; neovascular age-related macular degeneration; ranibizumab; real-world outcomes; treatment frequency; visual acuity.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Andrew A. Moshfeghi has served as a consultant to Allegro, Allergan, Alimera, Graybug, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Genentech, Clearside, Bausch, EyePoint, and Novartis and as a speaker for Allergan. He has also received research support from Allegro, Novartis, Genentech, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc and holds equity interest in Pr3vent, OptiSTENT, and Visunex. John D. Pitcher has served as a consultant to Allergan, Genentech, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc, and REGENXBIO and as a speaker for Genentech, Novartis, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. He has also received research support from Alcon. Genevieve Lucas was a salaried employee of Vestrum Health at the time that these analyses were undertaken. Nick Boucher is a salaried employee of Vestrum Health. Namrata Saroj was a salaried employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc at the time that these analyses were undertaken and is currently a paid consultant for Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Dr Saroj also serves as a consultant for Aerie, Allegro, Apellis, Adverum, and SamaCare and is an equity owner in Allegro, Pr3vent, and SamaCare.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, et al. ; MARINA Study Group. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(14):1419–1431. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa054481 - PubMed
-
- Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, et al. ; ANCHOR Study Group. Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(14):1432–1444. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa062655 - PubMed
-
- Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V, et al. ; VIEW 1 and VIEW 2 Study Groups. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF Trap-Eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(12):2537–2548. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.09.006 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

