Metabolomic Profiling of Lungs from Mice Reveals the Variability of Metabolites in Pneumocystis Infection and the Metabolic Abnormalities in BAFF-R-Deficient Mice
- PMID: 37006807
- PMCID: PMC10065423
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S394608
Metabolomic Profiling of Lungs from Mice Reveals the Variability of Metabolites in Pneumocystis Infection and the Metabolic Abnormalities in BAFF-R-Deficient Mice
Abstract
Purpose: The incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in patients without human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has been increasing. In this study, we aimed to investigate the metabolic changes in Pneumocystis infection and the metabolic abnormalities in B-cell-activating factor receptor (BAFF-R)-deficient mice with Pneumocystis infection.
Methods: The important function of B cells during Pneumocystis infection is increasingly recognized. In this study, a Pneumocystis-infected mouse model was constructed in BAFF-R-/- mice and wild-type (WT) mice. Lungs of uninfected WT C57BL/6, WT Pneumocystis-infected, and BAFF-R-/- Pneumocystis-infected mice were used for metabolomic analyses to compare the metabolomic profiles among the groups, with the aim of exploring the metabolic influence of Pneumocystis infection and the influence of mature B-cell deficiency during infection.
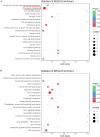
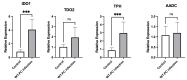
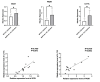
Results: The results indicated that many metabolites, mainly lipids and lipid-like molecules, were dysregulated in Pneumocystis-infected WT mice compared with uninfected WT C57BL/6 mice. The data also demonstrated significant changes in tryptophan metabolism, and the expression levels of key enzymes of tryptophan metabolism, such as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), were significantly upregulated. In addition, B-cell development and function might be associated with lipid metabolism. We found a lower level of alitretinoin and the abnormalities of fatty acid metabolism in BAFF-R-/- Pneumocystis-infected mice. The mRNA levels of enzymes associated with fatty acid metabolism in the lung were upregulated in BAFF-R-/- Pneumocystis-infected mice and positively correlated with the level of IL17A, thus suggesting that the abnormalities of fatty acid metabolism may be associated with greater inflammatory cell infiltration in the lung tissue of BAFF-R-/- Pneumocystis-infected mice compared with the WT Pneumocystis-infected mice.
Conclusion: Our data revealed the variability of metabolites in Pneumocystis-infected mice, suggesting that the metabolism plays a vital role in the immune response to Pneumocystis infection.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; Pneumocystis pneumonia; inflammation; metabolomics.
© 2023 Rong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Analysis of lncRNA and mRNA Repertoires in Lung From BAFF-R-Deficient Pneumocystis-Infected Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 10;13:898660. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.898660. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35774783 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10-producing B cells regulate Th1/Th17-cell immune responses in Pneumocystis pneumonia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 Jan 1;316(1):L291-L301. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00210.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30284926
-
B cell-activating factor regulates the survival of B lymphocytes infected with human cytomegalovirus.Immunol Lett. 2017 Jul;187:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.04.013. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28442365
-
Marginal Zone B-Cell Populations and Their Regulatory Potential in the Context of HIV and Other Chronic Inflammatory Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 21;23(6):3372. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063372. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Differences in Pneumocystis Pneumonia Infection Between HIV and Non-HIV Patients.Cureus. 2022 Aug 6;14(8):e27727. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27727. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36106266 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary metabolic changes in a rabbit model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia: insights from metabolomic analysis.BMC Microbiol. 2025 May 28;25(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04060-x. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40437385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grønseth S, Rogne T, Hannula R, Åsvold BO, Afset JE, Damås JK. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of immunocompromised patients infected with Pneumocystis jirovecii in a twelve-year retrospective study from Norway. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):659. doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06144-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

