Diagnosis and treatment of diffuse pulmonary lymphangioma in children: A case report
- PMID: 37006871
- PMCID: PMC10061045
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.11874
Diagnosis and treatment of diffuse pulmonary lymphangioma in children: A case report
Abstract
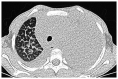
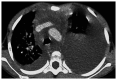
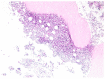
The present study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics of diffuse pulmonary lymphangioma (DPL) in children to improve the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. A case of pediatric DPL was observed for its clinical symptoms, imaging features, lung biopsy pathological characteristics and immunohistochemical phenotypes, and relevant literature was also reviewed. The main clinical manifestations of this pediatric patient were a cough, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, bloody chylothorax and pericardial effusion. Chest computed tomography showed a grid-like shadow and markedly thickened interlobular septa. Pathological examination revealed lymphatic vessel hyperplasia and expansion. Immunohistochemistry showed positive staining of lymphatic endothelial cells CD31 and D2-40. The patient's condition improved after combined treatment with methylprednisone, propranolol, sirolimus and somatostatin, whose bloody chylothorax also achieved good therapeutic effect after conservative treatment. Overall, the clinical and imaging appearances of DPL are lack of characterization, and its clinical manifestations include cough, shortness of breath and chylothorax. Computed tomography may show mesh-like shadows of both lungs and thickened interlobular septa. The definite diagnosis of DPL depends on biopsy pathology. In addition to this case, B-ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy is effective and safe, and propranolol-sirolimus treatment has a certain effect, but the clinical effect may be different. Conservative treatment of pleural effusion can result in better curative effect.
Keywords: children; diagnosis; diffuse pulmonary lymphangiomatosis; oncology; sirolimus.
Copyright: © Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
