Breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis): Processing, nutritional quality, and food applications
- PMID: 37006932
- PMCID: PMC10061028
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1156155
Breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis): Processing, nutritional quality, and food applications
Abstract
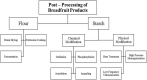
Breadfruit is an underutilized but highly nutritive crop containing complex carbohydrates while being low in fat. It is also a good source of essential amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine). With a better understanding of breadfruit's morphology, its potential as a global solution to food security has been gaining popularity. Breadfruit has been forecasted to have a larger amount of suitable cultivable land area compared to major crops such as rice and wheat, making its cultivation more desirable. Due to its highly perishable nature, good post-harvesting and post-processing practices are essential to extend the shelf life of breadfruit for global transportation and consumption. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review on various processing methods of flour and starch, nutritional significance and new food applications of this novel food staple. In this review, the effects of the different processing and post-processing methods of breadfruit flour and starch have been described, and the nutritional composition and application of breadfruit flour as an ingredient replacer in various food applications have been discussed. It is vital to understand the processing and post-processing methods of breadfruit flour to enhance its shelf-life, physicochemical and functional properties. Furthermore, a compilation of novel food applications has been done to promote its use in the food industry. In conclusion, breadfruit flour and starch are highly versatile for use in numerous food products with added health benefits.
Keywords: breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis); food applications; functional properties; ingredient replacer; nutritional; post-processing.
Copyright © 2023 Mehta, Quek and Henry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ragone D. Breadfruit for food and nutrition security in the 21st century. Trop Agric. (2016) 93:1–32.
-
- Roberts-Nkrumah L. editor. An overview of breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) in the Caribbean. Acta Hortic. (2007) 757:51–60. 10.17660/ActaHortic.2007.757.5 - DOI
-
- Aalbersberg W, Lovelace C, Madhoji K, Parkinson S. Davuke, the traditional Fijian method of pit preservation of staple carbohydrate foods. Ecol Food Nutr. (1988) 21:173–80. 10.1080/03670244.1988.9991030 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources