Pulsed electric fields-assisted extraction of valuable compounds from red grape pomace: Process optimization using response surface methodology
- PMID: 37006934
- PMCID: PMC10063923
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1158019
Pulsed electric fields-assisted extraction of valuable compounds from red grape pomace: Process optimization using response surface methodology
Abstract
Background: The application of Pulsed electric fields as a mild and easily scalable electrotechnology represents an effective approach to selectively intensify the extractability of bioactive compounds from grape pomace, one of the most abundant residues generated during the winemaking process.
Objective: This study addressed the optimization of the pulsed electric fields (PEF)-assisted extraction to enhance the extraction yields of bioactive compounds from red grape pomace using response surface methodology (RSM).
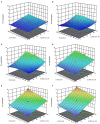
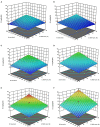
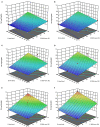
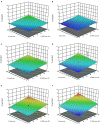
Methods: The cell disintegration index (Z p ) was identified as response variable to determine the optimal PEF processing conditions in terms of field strength (E = 0.5-5 kV/cm) and energy input (WT = 1-20 kJ/kg). For the solid-liquid extraction (SLE) process the effects of temperature (20-50°C), time (30-300min), and solvent concentration (0-50% ethanol in water) on total phenolic content (TPC), flavonoid content (FC), total anthocyanin content (TAC), tannin content (TC), and antioxidant activity (FRAP) of the extracts from untreated and PEF-treated plant tissues were assessed. The phenolic composition of the obtained extracts was determined via HPLC-PDA.
Results: Results demonstrated that the application of PEF at the optimal processing conditions (E = 4.6 kV/cm, WT = 20 kJ/kg) significantly enhanced the permeabilization degree of cell membrane of grape pomace tissues, thus intensifying the subsequent extractability of TPC (15%), FC (60%), TAC (23%), TC (42%), and FRAP values (31%) concerning the control extraction. HPLC-PDA analyses showed that, regardless of the application of PEF, the most abundant phenolic compounds were epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, and peonidin 3-O-glucoside, and no degradation of the specific compounds occurred upon PEF application.
Conclusion: The optimization of the PEF-assisted extraction process allowed to significantly enhance the extraction yields of high-value-added compounds from red grape pomace, supporting further investigations of this process at a larger scale.
Keywords: HPLC-PDA; bioactive compounds; green extraction; pulsed electric fields (PEF); red grape by-products; response surface methodology.
Copyright © 2023 Carpentieri, Ferrari and Pataro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


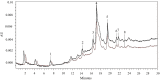
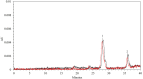
References
-
- Pataro G, Carullo D, Ferrari G. Innovative processes for the extraction of bioactive compounds from winery wastes and by-products. Imp Sust Viticult Winemaking Prac. (2022) 1:281–303. 10.1016/B978-0-323-85150-3.00004-9 - DOI
-
- Gubitosa J, Rizzi V, Laurenzana A, Scavone F, Frediani E, Fibbi G, et al. The “end life” of the grape pomace waste become the new beginning: the development of a virtuous cycle for the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and removal of emerging contaminants from water. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:994. 10.3390/antiox11050994 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

