Design, preparation, and in vitro evaluation of gastroretentive floating matrix tablet of mitiglinide
- PMID: 37006995
- PMCID: PMC10050700
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1140351
Design, preparation, and in vitro evaluation of gastroretentive floating matrix tablet of mitiglinide
Abstract
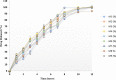
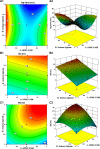
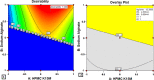
The present research is focused on developing floating matrix tablets of mitiglinide to prolong its gastric residence time for better absorption. Gastroretentive tablets were prepared using a direct compression technique with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose K15M (HPMC K15M) and sodium alginate as matrix-forming polymers and sodium bicarbonate as the gas-forming agent. A 32 full factorial design was adopted to optimize the flotation and release profile of the drug. The concentration of HPMC K15M and sodium alginate were taken as the independent variables, and the floating lag time, time required for 50% drug release, and time required for 90% drug release were taken as dependent variables. The compatibility between drug and excipients was assessed by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The prepared tablets were evaluated for different parameters such as hardness, friability, drug content, floating time, in vitro dissolution, and stability. Dissolution data were analyzed using various kinetic models to ascertain the mechanism of drug release. Finally, a radiographic study was conducted to estimate the retention time of the optimized floating matrix tablets of mitiglinide inside the body. The results revealed that all the physical properties of the developed formulations were within standard limits. The formulation M3, with the maximum amount of both independent variables, was considered to be the optimized formulation based on the desirability value. In addition, the optimized M3 formulation showed stability for over 6 months, as evidenced by insignificant changes in lag time, drug release pattern, and other physical properties. Furthermore, radiographic examination indicated that the tablets remained afloat in gastric fluid for up to 12 h in the rabbit's stomach. In conclusion, the developed floating matrix tablet of mitiglinide could be regarded as a promising formulation that could release the drug in the stomach at a controlled rate and, hence, offer better management of type II diabetes.
Keywords: factorial design; floating matrix tablet; gastroretentive; mitiglinide; radiography.
Copyright © 2023 Patel, Shelke, Surti, Panzade, Al-Keridis, Upadhyay, Alshammari and Saeed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Formulation and evaluation of different floating tablets containing metronidazole to target stomach.Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12(4):425-43. doi: 10.2174/156720181204150729125655. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25924732
-
Design and evaluation of gastroretentive levofloxacin floating mini-tablets-in-capsule system for eradication of Helicobacter pylori.Saudi Pharm J. 2014 Dec;22(6):570-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Saudi Pharm J. 2014. PMID: 25561871 Free PMC article.
-
Development of sustained release floating drug delivery system for norfloxacin: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2011 May-Jun;65(3):198-206. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2011.00685. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2011. PMID: 22293231
-
Formulation and evaluation of floating matrix tablet of stavudine.Int J Pharm Investig. 2012 Apr;2(2):83-9. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.100047. Int J Pharm Investig. 2012. PMID: 23119237 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation development, optimization, and evaluation of sustained release tablet of valacyclovir hydrochloride by combined approach of floating and swelling for better gastric retention.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2014 Dec;4(5-6):452-64. doi: 10.1007/s13346-014-0207-x. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 25787207
References
-
- Chen S., Zhu J., Cheng J. (2007). Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a novel combined multiparticulate delayed-onset sustained-release formulation of diltiazem hydrochloride. Die Pharmazie-An Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 62 (12), 907–913. - PubMed
-
- Damodharan N. (2020). Mathematical modelling of dissolution kinetics in dosage forms. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 13 (3), 1339–1345. 10.5958/0974-360x.2020.00247.4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

