Dendrimer: An update on recent developments and future opportunities for the brain tumors diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 37006997
- PMCID: PMC10060650
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1159131
Dendrimer: An update on recent developments and future opportunities for the brain tumors diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
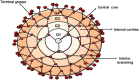
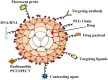
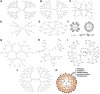
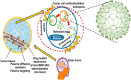
A brain tumor is an uncontrolled cell proliferation, a mass of tissue composed of cells that grow and divide abnormally and appear to be uncontrollable by the processes that normally control normal cells. Approximately 25,690 primary malignant brain tumors are discovered each year, 70% of which originate in glial cells. It has been observed that the blood-brain barrier (BBB) limits the distribution of drugs into the tumour environment, which complicates the oncological therapy of malignant brain tumours. Numerous studies have found that nanocarriers have demonstrated significant therapeutic efficacy in brain diseases. This review, based on a non-systematic search of the existing literature, provides an update on the existing knowledge of the types of dendrimers, synthesis methods, and mechanisms of action in relation to brain tumours. It also discusses the use of dendrimers in the diagnosis and treatment of brain tumours and the future possibilities of dendrimers. Dendrimers are of particular interest in the diagnosis and treatment of brain tumours because they can transport biochemical agents across the BBB to the tumour and into the brain after systemic administration. Dendrimers are being used to develop novel therapeutics such as prolonged release of drugs, immunotherapy, and antineoplastic effects. The use of PAMAM, PPI, PLL and surface engineered dendrimers has proven revolutionary in the effective diagnosis and treatment of brain tumours.
Keywords: brain targeting; brain tumor; brain tumor imaging; dendrimers; theranostics.
Copyright © 2023 Kaurav, Ruhi, Al-Goshae, Jeppu, Ramachandran, Sahu, Sarkar, Khan and Ashif Ikbal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adeli M., Rasoulian B., Saadatmehr F., Zabihi F. (2013). Hyperbranched poly (citric acid) and its application as anticancer drug delivery system. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 129 (6), 3665–3671. 10.1002/app.39028 - DOI
-
- Almalki Y. E., Ali M. U., Kallu K. D., Masud M., Zafar A., Alduraibi S. K., et al. (2022). Isolated convolutional-neural-network-based deep-feature extraction for brain tumor classification using shallow classifier. Diagn. (Basel, Switz. 12 (8), 1793. 10.3390/diagnostics12081793 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

